Featured
-
-
Research Briefing |
 Host–parasite dynamics in the liver stage of malaria
Host–parasite dynamics in the liver stage of malaria
Gene expression was assessed in individual liver cells from mice that were infected with the rodent-specific form of the malaria parasite. This revealed that infections of cells in the inner zones of the lobule units that make up the liver are more likely to succeed than are infections in the outer zones.
-
Article |
 A spatiotemporally resolved single-cell atlas of the Plasmodium liver stage
A spatiotemporally resolved single-cell atlas of the Plasmodium liver stage
Single-cell RNA sequencing and single-molecule RNA transcript imaging have been used to characterize spatially and temporally resolved mouse liver and parasite expression programmes during infection with the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei ANKA.
- Amichay Afriat
- , Vanessa Zuzarte-Luís
- & Shalev Itzkovitz
-
Research Briefing |
 Cancer cells move and spread faster in thicker extracellular fluids
Cancer cells move and spread faster in thicker extracellular fluids
The viscosity of extracellular fluid is a key physical cue, but its impact on cell function and cancer-cell dissemination has remained largely unknown. Experiments in various systems reveal that cancer cells sense, respond to and develop memory of the viscosity of extracellular fluid, with high viscosities increasing cell motility and promoting cancer dissemination.
-
News Feature |
 The shape-shifting blobs that shook up cell biology
The shape-shifting blobs that shook up cell biology
More than a decade ago, scientists started finding peculiar droplets inside cells. Now researchers are trying to work out how these ubiquitous beads form and what they do.
- Elie Dolgin
-
Article |
 Blocking PD-L1–PD-1 improves senescence surveillance and ageing phenotypes
Blocking PD-L1–PD-1 improves senescence surveillance and ageing phenotypes
PD-L1 expression by senescent cells renders them resistant to clearance by CD8 T cells, suggesting PD-L1 as a target for mitigating the effects of ageing.
- Teh-Wei Wang
- , Yoshikazu Johmura
- & Makoto Nakanishi
-
Article
| Open Access Histone H2B.8 compacts flowering plant sperm through chromatin phase separation
Histone H2B.8 compacts flowering plant sperm through chromatin phase separation
H2B.8 is identified as a histone variant that mediates a newly described mechanism of transcription-compatible chromatin condensation in flowering plant sperm cells.
- Toby Buttress
- , Shengbo He
- & Xiaoqi Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Extracellular fluid viscosity enhances cell migration and cancer dissemination
Extracellular fluid viscosity enhances cell migration and cancer dissemination
Elevated viscosity counterintuitively increases the motility of various cell types in vitro and imprints mechanical memory to tumour cells, which enables them to disseminate more efficiently in vivo.
- Kaustav Bera
- , Alexander Kiepas
- & Konstantinos Konstantopoulos
-
Article |
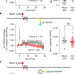 Non-canonical β-adrenergic activation of ERK at endosomes
Non-canonical β-adrenergic activation of ERK at endosomes
β2-adrenergic receptor(β2AR) signalling induces ERK activity at endosomes, but not at the plasma membrane, and this activity is dependent on active, endosome-localized Gαs and requires ligand-stimulated β2AR endocytosis.
- Yonghoon Kwon
- , Sohum Mehta
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the SEA complex
Cryo-EM structure of the SEA complex
The cryo-EM structure of the yeast SEA complex suggests that SEACAT functions as a scaffold for binding TORC1 regulators.
- Lucas Tafur
- , Kerstin Hinterndorfer
- & Robbie Loewith
-
Article
| Open Access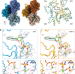 Bending forces and nucleotide state jointly regulate F-actin structure
Bending forces and nucleotide state jointly regulate F-actin structure
The nucleotide state of actin modulates F-actin structural transitions evoked by bending forces.
- Matthew J. Reynolds
- , Carla Hachicho
- & Gregory M. Alushin
-
News & Views |
 Assembly surprise for membrane proteins
Assembly surprise for membrane proteins
Membrane-spanning proteins have many crucial roles in the cell. New findings challenge our current understanding of the route by which such proteins are inserted into the membranes of animal cells.
- Ben C. Berks
-
Research Briefing |
 A protein that mobilizes the cofactor molecule haem for use in cells
A protein that mobilizes the cofactor molecule haem for use in cells
Haem, the molecule that gives blood its red colour, is crucial for nearly all life on Earth, but it can be toxic to cells. A protein called HRG-9 has a previously unrecognized role, in various species, in trafficking haem safely from sites where it is synthesized or stored to places where it can be used.
-
Article
| Open Access Substrate-driven assembly of a translocon for multipass membrane proteins
Substrate-driven assembly of a translocon for multipass membrane proteins
Biochemical reconstitution and functional analysis reveal how newly synthesized multipass membrane proteins dynamically remodel the translocon to facilitate their successful biogenesis.
- Arunkumar Sundaram
- , Melvin Yamsek
- & Robert J. Keenan
-
Article
| Open Access Clathrin-associated AP-1 controls termination of STING signalling
Clathrin-associated AP-1 controls termination of STING signalling
The adaptor protein AP-1 controls the shutdown of STING signalling through a mechanism in which AP-1 recognizes a dileucine motif in phosphorylated STING, which leads to targeted transport of STING to the endolysosomal system for degradation.
- Ying Liu
- , Pengbiao Xu
- & Andrea Ablasser
-
Article |
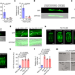 HRG-9 homologues regulate haem trafficking from haem-enriched compartments
HRG-9 homologues regulate haem trafficking from haem-enriched compartments
HRG-9 (also known as TANGO2) is an evolutionarily conserved haem chaperone that traffics haem from sites of storage or synthesis in eukaryotic cells.
- Fengxiu Sun
- , Zhenzhen Zhao
- & Caiyong Chen
-
Research Highlight |
 Why are some people mosquito magnets? Skin acids offer a hint
Why are some people mosquito magnets? Skin acids offer a hint
Experiments find a link between a person’s allure to the blood-sucking insects and specific molecules that waft from their skin.
-
Article |
 Activation of γ-globin expression by hypoxia-inducible factor 1α
Activation of γ-globin expression by hypoxia-inducible factor 1α
Detailed mechanistic insight into fetal globin gene induction during hypoxia-associated stress erythropoiesis provides new therapeutic approaches to treat β-haemoglobinopathies, such as sickle cell disease and β-thalassaemia.
- Ruopeng Feng
- , Thiyagaraj Mayuranathan
- & Mitchell J. Weiss
-
Article
| Open Access Collagenolysis-dependent DDR1 signalling dictates pancreatic cancer outcome
Collagenolysis-dependent DDR1 signalling dictates pancreatic cancer outcome
Cleaved and intact type I collagen have different effects on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), and remodelling of type I collagen—mediated through DDR1 signalling—is a prognostic indicator for the survival of patients with PDAC.
- Hua Su
- , Fei Yang
- & Michael Karin
-
Article |
 The γδ IEL effector API5 masks genetic susceptibility to Paneth cell death
The γδ IEL effector API5 masks genetic susceptibility to Paneth cell death
Intraepithelial lymphocytes expressing γ and δ T cell receptor subunits protect Paneth cells from cell death caused by viral infection or Crohn's disease.
- Yu Matsuzawa-Ishimoto
- , Xiaomin Yao
- & Ken Cadwell
-
Article |
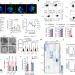 An LKB1–mitochondria axis controls TH17 effector function
An LKB1–mitochondria axis controls TH17 effector function
OPA1 regulates the formation of the distinct mitochondrial morphology observed in T helper 17 cells, which influences cytokine expression via LKB1.
- Francesc Baixauli
- , Klara Piletic
- & Erika L. Pearce
-
Article |
 CLN3 is required for the clearance of glycerophosphodiesters from lysosomes
CLN3 is required for the clearance of glycerophosphodiesters from lysosomes
The lysosomal transmembrane protein CLN3 is required for the lysosomal clearance of glycerophosphodiesters in mice and in human cells, suggesting that the loss of CLN3 causes Batten disease in children due to defects in glycerophospholipid metabolism.
- Nouf N. Laqtom
- , Wentao Dong
- & Monther Abu-Remaileh
-
Outlook |
 Prostate cancer: highlights from research
Prostate cancer: highlights from research
Gut microbes drive treatment resistance, fresh hope for immunotherapy, and other studies and clinical trials.
- Annette Fenner
-
Outlook |
 How to improve the diagnosis of prostate cancer
How to improve the diagnosis of prostate cancer
Prostate-specific antigen is an established biomarker, but it is flawed. Research into alternatives is starting to get results, but will they reduce mortality?
- Benjamin Plackett
-
Research Highlight |
 How cholesterol encourages a cell to bulk up
How cholesterol encourages a cell to bulk up
The molecule binds to a cellular protein, setting off a cascade of molecular activity that leads to cell growth.
-
News & Views |
 A plant auxin-binding protein resurfaces after a deep dive
A plant auxin-binding protein resurfaces after a deep dive
The hormone auxin regulates plant growth through nuclear co-receptors. A rapid response also occurs at the cell surface after auxin is perceived by the receptor TMK1 and a co-receptor protein. Is ABP1 this co-receptor?
- Angus S. Murphy
- & Wendy A. Peer
-
Article |
 A phosphoinositide signalling pathway mediates rapid lysosomal repair
A phosphoinositide signalling pathway mediates rapid lysosomal repair
Lysosomal membrane damage triggers a lipid signalling pathway that repairs lysosomes via lipid transport at newly established endoplasmic reticulum–lysosomal membrane contact sites.
- Jay Xiaojun Tan
- & Toren Finkel
-
Article
| Open Access A microbial supply chain for production of the anti-cancer drug vinblastine
A microbial supply chain for production of the anti-cancer drug vinblastine
De novo microbial biosynthesis of vindoline and catharanthine using a highly engineered yeast and in vitro chemical coupling to vinblastine is carried out, positioning yeast as a scalable platform to produce many monoterpene indole alkaloids.
- Jie Zhang
- , Lea G. Hansen
- & Jay D. Keasling
-
News & Views |
 A biochemical timer phases condensates in and out in cells
A biochemical timer phases condensates in and out in cells
The interior of the cell is organized with the help of dynamic structures that condense like droplets. A timing strategy ensures that cells maintain healthy function by avoiding uncontrolled growth of these condensates.
- Guillaume Charras
- & Martin Lenz
-
Article
| Open Access Endocytosis in the axon initial segment maintains neuronal polarity
Endocytosis in the axon initial segment maintains neuronal polarity
Endocytosis and degradation of plasma membrane proteins in the axon initial segment, together with the diffusion-barrier mechanism, maintain a polarized distribution of plasma membrane proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans, mouse, rat and human neurons.
- Kelsie Eichel
- , Takeshi Uenaka
- & Kang Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Post-translational control of beige fat biogenesis by PRDM16 stabilization
Post-translational control of beige fat biogenesis by PRDM16 stabilization
The ubiquitin E3 ligase CUL2–APPBP2 determines PRDM16 protein stability by catalysing PRDM16 polyubiquitination in beige fat.
- Qiang Wang
- , Huixia Li
- & Shingo Kajimura
-
Research Briefing |
 Neurons shape the identity of microglia in the brain
Neurons shape the identity of microglia in the brain
Microglia are immune cells that regulate the function and activity of the nervous system. Detailed molecular and spatial studies in mice reveal that different types of neuron govern the density and states of nearby microglia, interactions that can shape local neural circuits.
-
Article
| Open Access Truncated FGFR2 is a clinically actionable oncogene in multiple cancers
Truncated FGFR2 is a clinically actionable oncogene in multiple cancers
Truncation of exon 18 of FGFR2 (FGFR2ΔE18) is a potent driver mutation in mice and humans, and FGFR-targeted therapy should be considered for patients with cancer expressing stable FGFR2ΔE18 variants.
- Daniel Zingg
- , Jinhyuk Bhin
- & Jos Jonkers
-
Article
| Open Access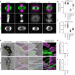 A mitotic chromatin phase transition prevents perforation by microtubules
A mitotic chromatin phase transition prevents perforation by microtubules
Histone deacetylation at the onset of mitosis induces a chromatin-intrinsic phase transition that endows chromosomes with the physical characteristics necessary for their precise movement during cell division.
- Maximilian W. G. Schneider
- , Bryan A. Gibson
- & Daniel W. Gerlich
-
News & Views |
 A phase transition for chromosome transmission when cells divide
A phase transition for chromosome transmission when cells divide
An analysis of chromosomes during mitotic cell division reveals that DNA and associated histone proteins condense through a process called phase transition, which helps them to resist the pushing forces involved in mitosis.
- Kazuhiro Maeshima
-
Article
| Open Access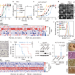 A non-canonical vitamin K cycle is a potent ferroptosis suppressor
A non-canonical vitamin K cycle is a potent ferroptosis suppressor
Biochemical and lipidomic analyses identify an anti-ferroptotic function of vitamin K and reveal ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1) as the enzyme mediating warfarin-resistant vitamin K reduction in the canonical vitamin K cycle.
- Eikan Mishima
- , Junya Ito
- & Marcus Conrad
-
Article
| Open Access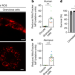 Oocytes maintain ROS-free mitochondrial metabolism by suppressing complex I
Oocytes maintain ROS-free mitochondrial metabolism by suppressing complex I
Oocytes prevent the production of reactive oxygen species by remodelling the mitochondrial electron transport chain through elimination of complex I, a strategy that enables their long-term viability.
- Aida Rodríguez-Nuevo
- , Ariadna Torres-Sanchez
- & Elvan Böke
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear chromosome locations dictate segregation error frequencies
Nuclear chromosome locations dictate segregation error frequencies
Using single-cell DNA sequencing after an error-prone mitosis in untransformed, diploid cell lines and organoids, chromosomes are shown to have different segregation error frequencies that result in non-random aneuploidy landscapes.
- Sjoerd J. Klaasen
- , My Anh Truong
- & Geert J. P. L. Kops
-
News & Views |
 Location in the nucleus foretells chromosome anomalies
Location in the nucleus foretells chromosome anomalies
A single-cell analysis suggests that the 3D location of chromosomes in the cell nucleus contributes to their likelihood of being involved in genomic rearrangements associated with cancer.
- Krishnendu Guin
- & Tom Misteli
-
Article |
 Structure of the nutrient-sensing hub GATOR2
Structure of the nutrient-sensing hub GATOR2
The 3D structure of the human nutrient-sensing complex GATOR2 is resolved using cryo-electron microscopy.
- Max L. Valenstein
- , Kacper B. Rogala
- & David M. Sabatini
-
Article
| Open Access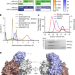 Structure of the MRAS–SHOC2–PP1C phosphatase complex
Structure of the MRAS–SHOC2–PP1C phosphatase complex
A structure of the MRAS–SHOC2–PP1C complex supports a RAS-driven and multi-molecular model for RAF activation in which individual RAS–GTP molecules recruit RAF–14-3-3 and SHOC2–PP1C to activate the downstream pathway.
- Zachary J. Hauseman
- , Michelle Fodor
- & Daniel A. King
-
Article |
 Mechanisms and inhibition of Porcupine-mediated Wnt acylation
Mechanisms and inhibition of Porcupine-mediated Wnt acylation
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of human Porcupine in complex with palmitoleoyl-coenzyme A, the inhibitor LGK974 and its peptide substrate suggest a mechanism for Wnt acylation.
- Yang Liu
- , Xiaofeng Qi
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Article |
 Retrograde movements determine effective stem cell numbers in the intestine
Retrograde movements determine effective stem cell numbers in the intestine
Small intestinal crypts contain twice as many effective stem cells as large intestinal crypts, and this difference is determined by the degree of Wnt-driven retrograde cell movement—which is largely absent in the large intestine—counteracting conveyor-belt-like upward movement.
- Maria Azkanaz
- , Bernat Corominas-Murtra
- & Jacco van Rheenen
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell roadmap of human gonadal development
Single-cell roadmap of human gonadal development
This study provides a comprehensive spatiotemporal map of human and mouse gonadal differentiation, using a combination of single-cell and spatial transcriptomics, chromatin accessibility assays and fluorescent microscopy, which can guide in vitro gonadogenesis.
- Luz Garcia-Alonso
- , Valentina Lorenzi
- & Roser Vento-Tormo
-
Article
| Open Access Apoptotic brown adipocytes enhance energy expenditure via extracellular inosine
Apoptotic brown adipocytes enhance energy expenditure via extracellular inosine
Untargeted metabolomics demonstrate that apoptotic brown adipocytes release a specific pattern of metabolites with purine metabolites being highly enriched, and inosine is identified as a metabolite released during apoptosis regulating thermogenic fat and counteracting obesity.
- Birte Niemann
- , Saskia Haufs-Brusberg
- & Alexander Pfeifer
-
Article
| Open Access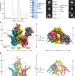 A peroxisomal ubiquitin ligase complex forms a retrotranslocation channel
A peroxisomal ubiquitin ligase complex forms a retrotranslocation channel
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the membrane-embedded ubiquitin ligase complex reveals its function as a retrotranslocation channel for shuttling mobile receptors out of peroxisomes.
- Peiqiang Feng
- , Xudong Wu
- & Tom A. Rapoport
-
Article |
 GREM1 is required to maintain cellular heterogeneity in pancreatic cancer
GREM1 is required to maintain cellular heterogeneity in pancreatic cancer
The BMP inhibitor GREM1 is a key regulator of cellular heterogeneity in pancreatic cancer in human and mouse.
- Linxiang Lan
- , Theodore Evan
- & Axel Behrens
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial RNA modifications shape metabolic plasticity in metastasis
Mitochondrial RNA modifications shape metabolic plasticity in metastasis
- Sylvain Delaunay
- , Gloria Pascual
- & Michaela Frye
-
Article |
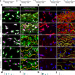 YAP/TAZ activity in stromal cells prevents ageing by controlling cGAS–STING
YAP/TAZ activity in stromal cells prevents ageing by controlling cGAS–STING
tDeclining YAP/TAZ mechanotransduction drives ageing by unleashing cGAS–STING signalling, a pillar of innate immunity, so sustaining YAP/TAZ mechanosignalling or inhibiting STING present promising approaches for limiting senescence-associated inflammation and improving healthy ageing.
- Hanna Lucie Sladitschek-Martens
- , Alberto Guarnieri
- & Stefano Piccolo
-
Outlook |
 Olfactory receptors are not unique to the nose
Olfactory receptors are not unique to the nose
The hundreds of receptors that give us our sense of smell have been found to have important roles in other parts of the body, and the prospect of targeting them with drugs is growing.
- Liam Drew
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Autophagy
- Cell adhesion
- Cell death
- Cell division
- Cell growth
- Cell migration
- Cell polarity
- Cell signalling
- Cellular imaging
- Chromosomes
- Circadian rhythms
- Cytoskeleton
- Glycobiology
- Mechanisms of disease
- Membrane trafficking
- Nuclear organization
- Nuclear transport
- Organelles
- Post-translational modifications
- Protein folding
- Protein transport
- Proteolysis
- Senescence

 MYC multimers shield stalled replication forks from RNA polymerase
MYC multimers shield stalled replication forks from RNA polymerase