Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Charge transfer observed in light-activated catalyst particles
Charge transfer observed in light-activated catalyst particles
The movement of electric charges in light-activated catalyst particles is key to the water-splitting reaction, which could be used to generate hydrogen as a renewable fuel. Such movement has now been observed in exquisite detail.
- Ulrich Aschauer
-
Article |
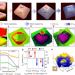 Spatiotemporal imaging of charge transfer in photocatalyst particles
Spatiotemporal imaging of charge transfer in photocatalyst particles
Photovoltage measurements on cuprous oxide photocatalyst particles are used to spatiotemporally track the charge transfer processes on the femtosecond to second timescale at the single-particle level.
- Ruotian Chen
- , Zefeng Ren
- & Can Li
-
News & Views |
 A leap forward in the quest for general catalysts
A leap forward in the quest for general catalysts
Truly general chemical reactions work well regardless of the structural features and functional groups in the starting molecule. A new screening protocol speeds up the identification of such reactions in the field of asymmetric catalysis.
- Manuel J. Scharf
- & Benjamin List
-
Article |
 Enantioselective [2+2]-cycloadditions with triplet photoenzymes
Enantioselective [2+2]-cycloadditions with triplet photoenzymes
Triplet photoenzymes developed through genetic encoding and directed evolution result in excited-state photocatalysts that provide a valuable approach to enantioselective photochemical synthesis.
- Ningning Sun
- , Jianjian Huang
- & Yuzhou Wu
-
Article |
 A designed photoenzyme for enantioselective [2+2] cycloadditions
A designed photoenzyme for enantioselective [2+2] cycloadditions
A genetically encoded triplet photosensitizer is used to develop an efficient photoenzyme that can promote enantioselective intramolecular and bimolecular [2+2] cycloadditions by means of triplet energy transfer.
- Jonathan S. Trimble
- , Rebecca Crawshaw
- & Anthony P. Green
-
News & Views |
 Synergistic active sites observed in a solid catalyst
Synergistic active sites observed in a solid catalyst
A solid catalyst has been prepared in which pairs of active sites work synergistically to promote an industrial chemical reaction, and the mechanism has been determined — a breakthrough for ‘pair site’ catalysis.
- Tiefeng Wang
-
Article |
 Bifunctional hydroformylation on heterogeneous Rh-WOx pair site catalysts
Bifunctional hydroformylation on heterogeneous Rh-WOx pair site catalysts
Catalysts consisting of oxide-supported pair sites can enable bifunctional reaction mechanisms with high activity and selectivity for reactions and so overcome the limitations in industry imposed by the use of homogeneous catalysts.
- Insoo Ro
- , Ji Qi
- & Phillip Christopher
-
Article |
 Screening for generality in asymmetric catalysis
Screening for generality in asymmetric catalysis
The analytical workflow outlined in this study allows multiple crude reaction mixtures to be analysed simultaneously, with substantial reductions in method development and analysis time, and maximizes the chances of finding catalytic systems with broad substrate scope.
- Corin C. Wagen
- , Spencer E. McMinn
- & Eric N. Jacobsen
-
Article |
 Tandem electrocatalytic N2 fixation via proton-coupled electron transfer
Tandem electrocatalytic N2 fixation via proton-coupled electron transfer
Using a molecular catalyst and a proton–electron transfer mediator in tandem delivers efficient electroreduction of nitrogen to ammonia at modest potentials, an approach that could be used to improve other important reactions.
- Pablo Garrido-Barros
- , Joseph Derosa
- & Jonas C. Peters
-
Article |
 An asymmetric sp3–sp3 cross-electrophile coupling using ‘ene’-reductases
An asymmetric sp3–sp3 cross-electrophile coupling using ‘ene’-reductases
A highly chemoselective and enantioselective cross-electrophile coupling using ‘ene’-reductases is reported, and photoexcited enzymes demonstrate the ability to carry out reactions between electrophiles that are not known for small-molecule catalysis.
- Haigen Fu
- , Jingzhe Cao
- & Todd K. Hyster
-
Article |
 Molecular editing of aza-arene C–H bonds by distance, geometry and chirality
Molecular editing of aza-arene C–H bonds by distance, geometry and chirality
A unified catalytic remote-directing template strategy enabled precise differentiation of remote and adjacent C6–H and C7–H bonds, and similar C3–H and C7–H bonds of a pharmaceutically relevant bicyclic aza-arene scaffold.
- Zhoulong Fan
- , Xiangyang Chen
- & Jin-Quan Yu
-
Article |
 Electrocatalytic metal hydride generation using CPET mediators
Electrocatalytic metal hydride generation using CPET mediators
Concerted proton–electron transfer mediators enable facile electrochemical metal hydride formation and thus improve CO2 reduction to useful chemicals, and could benefit a range of catalytic reactions involving metal hydride intermediates.
- Subal Dey
- , Fabio Masero
- & Victor Mougel
-
Article |
 Site-selective, stereocontrolled glycosylation of minimally protected sugars
Site-selective, stereocontrolled glycosylation of minimally protected sugars
A simplified synthesis strategy for stereo- and site-selective glycosylations, using minimally protected mono- and disaccharides and thiourea small-molecule catalysts, enables highly selective functionalization of carbohydrates.
- Qiuhan Li
- , Samuel M. Levi
- & Eric N. Jacobsen
-
Review Article |
 The road to fully programmable protein catalysis
The road to fully programmable protein catalysis
Recent progress in computational enzyme design, active site engineering and directed evolution are reviewed, highlighting methodological innovations needed to deliver improved designer biocatalysts.
- Sarah L. Lovelock
- , Rebecca Crawshaw
- & Anthony P. Green
-
Article |
 Cobalt-electrocatalytic HAT for functionalization of unsaturated C–C bonds
Cobalt-electrocatalytic HAT for functionalization of unsaturated C–C bonds
A perspective is given on how an electrocatalytic approach, inspired by decades of energy storage studies, can be used in the context of efficient cobalt-hydride generation with a variety of applications in modern organic synthesis.
- Samer Gnaim
- , Adriano Bauer
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article
| Open Access Organocatalytic stereoselective cyanosilylation of small ketones
Organocatalytic stereoselective cyanosilylation of small ketones
The development of confined organocatalysts for the enantioselective cyanosilylation of small, unbiased substrates, including 2-butanone, is shown to lead to catalysts that are as selective as enzymes, with excellent levels of control.
- Hui Zhou
- , Yu Zhou
- & Benjamin List
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic synthesis of phenols with nitrous oxide
Catalytic synthesis of phenols with nitrous oxide
A study demonstrates that nitrous oxide can act as the source of O in a catalytic conversion of aryl halides to phenols, releasing N2 as by-product.
- Franck Le Vaillant
- , Ana Mateos Calbet
- & Josep Cornella
-
Article |
 Multifunctional biocatalyst for conjugate reduction and reductive amination
Multifunctional biocatalyst for conjugate reduction and reductive amination
A biocatalytic enzyme originating from bacteria, EneIRED, facilitates amine-activated conjugate alkene reduction followed by reductive amination, efficiently preparing chiral amine diastereomers, which are commonly used in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
- Thomas W. Thorpe
- , James R. Marshall
- & Nicholas J. Turner
-
Article |
 Intermolecular [2π+2σ]-photocycloaddition enabled by triplet energy transfer
Intermolecular [2π+2σ]-photocycloaddition enabled by triplet energy transfer
A strain-release approach, realized by visible-light-mediated triplet energy transfer catalysis, enabled an intermolecular [2π+2σ]-photocycloaddition.
- Roman Kleinmans
- , Tobias Pinkert
- & Frank Glorius
-
News & Views |
 Self-assembly of molecules triggered by electricity
Self-assembly of molecules triggered by electricity
The options for controlling molecular self-assembly processes have been limited. A fresh approach uses electrons to facilitate self-assembly, and thereby provides precise external control over the process.
- Robert Francke
-
Article |
 Electron-catalysed molecular recognition
Electron-catalysed molecular recognition
A simple and versatile strategy is established to facilitate molecular recognition by extending electron catalysis for use in supramolecular non-covalent chemistry.
- Yang Jiao
- , Yunyan Qiu
- & J. Fraser Stoddart
-
Article |
 Biocatalytic oxidative cross-coupling reactions for biaryl bond formation
Biocatalytic oxidative cross-coupling reactions for biaryl bond formation
A study presents a biocatalytic method for the formation of sterically hindered biaryl bonds, providing a tunable approach for assembling molecules with catalyst-controlled reactivity, site selectivity and atroposelectivity.
- Lara E. Zetzsche
- , Jessica A. Yazarians
- & Alison R. H. Narayan
-
Article |
 Synthesis of chiral sulfinate esters by asymmetric condensation
Synthesis of chiral sulfinate esters by asymmetric condensation
A synthetic strategy for the stereoselective preparation of sulfinate esters and related sulfur stereogenic centres via asymmetric condensation expands the drug discovery toolbox for these compounds.
- Xin Zhang
- , Esther Cai Xia Ang
- & Choon-Hong Tan
-
Article |
 Automated iterative Csp3–C bond formation
Automated iterative Csp3–C bond formation
Identification of a hyperstable boronate enables automated lego-like synthesis to access a wider range of three-dimensionally complex small organic molecules rich in Csp3–C bonds.
- Daniel J. Blair
- , Sriyankari Chitti
- & Martin D. Burke
-
Article |
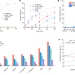 Au–Pd separation enhances bimetallic catalysis of alcohol oxidation
Au–Pd separation enhances bimetallic catalysis of alcohol oxidation
‘Cooperative redox enhancement (CORE) effects, which arise through the coupling of oxidative dehydrogenation and oxygen reduction reactions, can lead to increased rates of reaction over spatially separated bimetallic heterogeneous catalysts.
- Xiaoyang Huang
- , Ouardia Akdim
- & Graham J. Hutchings
-
Article |
 Time-resolved structural analysis of an RNA-cleaving DNA catalyst
Time-resolved structural analysis of an RNA-cleaving DNA catalyst
Using high-resolution NMR characterization, the kinetics and dynamics of the catalytic function of a DNAzyme are shown.
- Jan Borggräfe
- , Julian Victor
- & Manuel Etzkorn
-
Article
| Open Access Tritiation of aryl thianthrenium salts with a molecular palladium catalyst
Tritiation of aryl thianthrenium salts with a molecular palladium catalyst
The isotopic label tritium can be selectively added into aromatic organic compounds by a homogenous hydrogenolysis reaction using aryl thianthrenium salts, tritium gas and a molecular palladium catalyst.
- Da Zhao
- , Roland Petzold
- & Tobias Ritter
-
News & Views |
 Choreographing water molecules to speed up hydrogen production
Choreographing water molecules to speed up hydrogen production
A technical feat reveals subtle changes in water structure that can accelerate hydrogen production at an electrode interface. The catalytic process could be developed to help boost supply of this clean fuel.
- Matthias M. Waegele
-
Article
| Open Access In situ formation of ZnOx species for efficient propane dehydrogenation
In situ formation of ZnOx species for efficient propane dehydrogenation
Propene is obtained through propane dehydrogenation using catalysts that are toxic, expensive or demanding to regenerate with ecologically harmful compounds, but the ZnO-based alternative reported here is cheap, clean and scalable.
- Dan Zhao
- , Xinxin Tian
- & Evgenii V. Kondratenko
-
News & Views |
 Platinum catalysts strained controllably by size-changing nanocubes
Platinum catalysts strained controllably by size-changing nanocubes
The distance between the surface atoms of noble metals, such as platinum, affects the catalytic activity of these elements. An experimental approach using nanoparticles enables this effect to be systematically controlled and measured.
- Sylvain Brimaud
-
Article |
 Mastering the surface strain of platinum catalysts for efficient electrocatalysis
Mastering the surface strain of platinum catalysts for efficient electrocatalysis
By depositing platinum shells on palladium-based nanocubes, the strain can be controlled by through phosphorization and dephosphorization, making it possible to tune the electrocatalytic activity of the platinum shells.
- Tianou He
- , Weicong Wang
- & Mingshang Jin
-
Research Highlight |
 An iron grip could help pee to produce electricity
An iron grip could help pee to produce electricity
Catalyst based on nickel and iron allows electrical current to be harvested from the breakdown of urea.
-
News & Views |
 Benzene rings broken for chemical synthesis
Benzene rings broken for chemical synthesis
Benzene rings are almost unbreakable in typical reaction conditions. Chemistry has now been developed that selectively breaks these rings open, highlighting their potential as building blocks for making open-chain molecules.
- Mark R. Crimmin
-
Article |
 Metallaphotoredox-enabled deoxygenative arylation of alcohols
Metallaphotoredox-enabled deoxygenative arylation of alcohols
A metallaphotoredox-based cross-coupling platform is capable of activating a wide range of free alcohols using N-heterocyclic carbene salts, cleaving C–O bonds to form free carbon radicals that are then used to form new C–C bonds.
- Zhe Dong
- & David W. C. MacMillan
-
Article |
 Cleaving arene rings for acyclic alkenylnitrile synthesis
Cleaving arene rings for acyclic alkenylnitrile synthesis
Common aromatic rings, such as anilines, arylboronic acids and aryl halides, can be opened up and converted to alkenyl nitriles through carbon–carbon bond cleavage using a copper catalyst.
- Xu Qiu
- , Yueqian Sang
- & Ning Jiao
-
Article |
 Photoinduced copper-catalysed asymmetric amidation via ligand cooperativity
Photoinduced copper-catalysed asymmetric amidation via ligand cooperativity
In the presence of three ligands and light, two distinct copper catalysts combine to produce enantioenriched secondary amides from racemic alkyl electrophiles and primary amide nucleophiles.
- Caiyou Chen
- , Jonas C. Peters
- & Gregory C. Fu
-
Outlook |
 Better catalysts from super-fast heating
Better catalysts from super-fast heating
Start-up company HighT-Tech has developed a technique to make alloys that could improve catalysts or be used to build better batteries. The company is the winner of The Spinoff Prize 2021.
- Neil Savage
-
Article |
 A radical approach for the selective C–H borylation of azines
A radical approach for the selective C–H borylation of azines
Selective borylation of azines—nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycles used in the synthesis of many pharmaceuticals—is made possible by forming a radical from an aminoborane using a photocatalyst.
- Ji Hye Kim
- , Timothée Constantin
- & Daniele Leonori
-
Article |
 Discovery, characterization and engineering of ligases for amide synthesis
Discovery, characterization and engineering of ligases for amide synthesis
A family of enzymes—coronafacic acid ligases, involved in the synthesis of bacterial phytotoxins—are found to catalyse amide bond formation with a wide range of substrates.
- Michael Winn
- , Michael Rowlinson
- & Jason Micklefield
-
Article |
 A stable low-temperature H2-production catalyst by crowding Pt on α-MoC
A stable low-temperature H2-production catalyst by crowding Pt on α-MoC
A stable, low-temperature water–gas shift catalyst is achieved by crowding platinum atoms and clusters on α-molybdenum carbide; the crowding protects the support from oxidation that would cause catalyst deactivation.
- Xiao Zhang
- , Mengtao Zhang
- & Ding Ma
-
Article |
 Key role of chemistry versus bias in electrocatalytic oxygen evolution
Key role of chemistry versus bias in electrocatalytic oxygen evolution
Spectroscopic studies and theoretical calculations of the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction establish that reaction rates depend on the amount of charge stored in the electrocatalyst, and not on the applied potential.
- Hong Nhan Nong
- , Lorenz J. Falling
- & Travis E. Jones
-
Article |
 Catalytic asymmetric addition of an amine N–H bond across internal alkenes
Catalytic asymmetric addition of an amine N–H bond across internal alkenes
Hydroamination with high enantio- and regioselectivity is achieved across a wide range of internal alkenes by using a cationic iridium complex that adds an ammonia surrogate containing a pyridine group.
- Yumeng Xi
- , Senjie Ma
- & John F. Hartwig
-
News & Views |
 Fresh evidence challenges the consensus view of active sites in an industrial catalyst
Fresh evidence challenges the consensus view of active sites in an industrial catalyst
A study of the industrial catalyst titanium silicalite-1 suggests that the conventional view of the structure of its active sites is wrong. The findings might enable further optimization of related industrial catalysts.
- Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article |
 Metal-free photoinduced C(sp3)–H borylation of alkanes
Metal-free photoinduced C(sp3)–H borylation of alkanes
Metal-free borylation of C(sp3)–H bonds by violet-light-induced hydrogen atom transfer is reported, demonstrating high selectivity for the substitution of methyl C–H bonds over other weaker C–H bonds.
- Chao Shu
- , Adam Noble
- & Varinder K. Aggarwal
-
Article |
 Efficient epoxidation over dinuclear sites in titanium silicalite-1
Efficient epoxidation over dinuclear sites in titanium silicalite-1
A combination of spectroscopy, microscopy and theoretical calculations shows that the reactivity of titanium silicalite-1 as an epoxidation catalyst is due to the presence of dinuclear titanium sites.
- Christopher P. Gordon
- , Hauke Engler
- & Christophe Copéret
-
Article |
 Light-driven post-translational installation of reactive protein side chains
Light-driven post-translational installation of reactive protein side chains
A wide range of side chains are installed into proteins by addition of photogenerated alkyl or difluroalkyl radicals, providing access to new functionality and reactivity in proteins.
- Brian Josephson
- , Charlie Fehl
- & Benjamin G. Davis
-
Article |
 Rare-earth–platinum alloy nanoparticles in mesoporous zeolite for catalysis
Rare-earth–platinum alloy nanoparticles in mesoporous zeolite for catalysis
Alloy nanoparticles of platinum and rare-earth elements are formed using zeolites with pore-wall defects, producing stable, highly active and selective catalysts for the propane dehydrogenation reaction.
- Ryong Ryoo
- , Jaeheon Kim
- & Jae Won Shin
-
Article |
 Filling metal–organic framework mesopores with TiO2 for CO2 photoreduction
Filling metal–organic framework mesopores with TiO2 for CO2 photoreduction
Investigation of a chromium-based metal–organic framework shows that the location of added TiO2 inside specific mesopores strongly affects the ability of the material to catalyse photoreduction of CO2.
- Zhuo Jiang
- , Xiaohui Xu
- & Hexiang Deng
-
Article |
 Intercepting fleeting cyclic allenes with asymmetric nickel catalysis
Intercepting fleeting cyclic allenes with asymmetric nickel catalysis
Asymmetric nickel catalysis is used to intercept transient cyclic allene intermediates to achieve stereocontrol.
- Michael M. Yamano
- , Andrew V. Kelleghan
- & Neil K. Garg

 Heat and bacteria recycle mixed plastics into useful chemicals
Heat and bacteria recycle mixed plastics into useful chemicals