Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access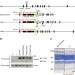 A point mutation in Semaphorin 4A associates with defective endosomal sorting and causes retinal degeneration
A point mutation in Semaphorin 4A associates with defective endosomal sorting and causes retinal degeneration
Semaphorin 4A is implicated in photoreceptor survival. Nojima and colleagues generate transgenic mice with different mutations in the Sema4A gene and find that point mutation of F350 causes severe degeneration in photoreceptor cells, which can be rescued by virus-mediated gene therapy.
- Satoshi Nojima
- , Toshihiko Toyofuku
- & Atsushi Kumanogoh
-
Article |
 Modular optimization of multi-gene pathways for fatty acids production in E. coli
Modular optimization of multi-gene pathways for fatty acids production in E. coli
Microbial fatty acid-derived fuels represent promising alternatives to the traditionally used fossil fuels. Koffas and colleagues report that E. colicentral metabolism can be modified to produce large quantities of fatty acids through a modular pathway engineering strategy.
- Peng Xu
- , Qin Gu
- & Mattheos A.G. Koffas
-
Article |
 Selective escape of proteins from the mitochondria during mitophagy
Selective escape of proteins from the mitochondria during mitophagy
Damaged mitochondria are eliminated from the cell by a form of autophagy called mitophagy. Here the authors show that during mitophagy, specific proteins are rescued from degradation by evacuation from the mitochondria to the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Shotaro Saita
- , Michiko Shirane
- & Keiichi I. Nakayama
-
Article |
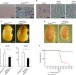 The phosphatase Dullard negatively regulates BMP signalling and is essential for nephron maintenance after birth
The phosphatase Dullard negatively regulates BMP signalling and is essential for nephron maintenance after birth
Kidney maintenance and function are essential for a healthy organism. Here Nishinakamura and colleagues show that the phosphatase Dullard suppresses BMP signalling and apoptosis in the mouse kidney and that Dullard is required for the maintenance of functional nephrons after birth.
- Masaji Sakaguchi
- , Sazia Sharmin
- & Ryuichi Nishinakamura
-
Article |
 The impact of free-ranging domestic cats on wildlife of the United States
The impact of free-ranging domestic cats on wildlife of the United States
Free-ranging domestic cats cause wildlife extinctions on islands, but their impact on wildlife in mainland areas is unclear. This study presents an estimate of mortality caused by cats in the United States, suggesting that 1.4–3.7 billion birds and 6.9–20.7 billion mammals are killed annually.
- Scott R. Loss
- , Tom Will
- & Peter P. Marra
-
Article |
 Deep proteome profiling of Trichoplax adhaerens reveals remarkable features at the origin of metazoan multicellularity
Deep proteome profiling of Trichoplax adhaerens reveals remarkable features at the origin of metazoan multicellularity
Trichoplaxis the most primitive multicellular animal on Earth and thus provides insight into the earliest stages of evolution. Delving deep into the proteome, Heck and colleagues observe a burst in tyrosine phosphorylation, confirming the hypothesis that at the onset of this new communication system a surplus of phosphorylation took place.
- Jeffrey H. Ringrose
- , Henk W.P. van den Toorn
- & Albert J.R. Heck
-
Article
| Open Access Computational identification of a transiently open L1/S3 pocket for reactivation of mutant p53
Computational identification of a transiently open L1/S3 pocket for reactivation of mutant p53
About 40% of human cancers carry missense mutations in the tumour suppressor protein p53. Here the authors identify a transiently open pocket in the protein, and by targeting a small molecule to it, partially restore mutant p53 tumour suppressor activity.
- Christopher D. Wassman
- , Roberta Baronio
- & Rommie E. Amaro
-
Article |
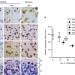 Heat shock factor-1 influences pathological lesion distribution of polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration
Heat shock factor-1 influences pathological lesion distribution of polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration
Heat shock factor-1 is a transcriptional regulator of heat shock proteins that is implicated in neurodegeneration. Kondo and colleagues study the effects of deleting heat shock factor-1 in a mouse model of muscular dystrophy and find that this augments the condition via the accumulation of androgen receptors.
- Naohide Kondo
- , Masahisa Katsuno
- & Gen Sobue
-
Article |
 Plant tumour biocontrol agent employs a tRNA-dependent mechanism to inhibit leucyl-tRNA synthetase
Plant tumour biocontrol agent employs a tRNA-dependent mechanism to inhibit leucyl-tRNA synthetase
Agrobacterium radiobacter strain K84 generates an antibiotic targeting pathogenic strains of Agrobacterium tumefaciens, enabling its use as a biocontrol to prevent infection of crops. Here the authors show that this antibiotic inhibits leucyl-tRNA synthetases via an unusual mechanism that depends on binding of tRNALeu.
- Shaileja Chopra
- , Andrés Palencia
- & John S. Reader
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro fabrication of functional three-dimensional tissues with perfusable blood vessels
In vitro fabrication of functional three-dimensional tissues with perfusable blood vessels
Artificially engineered tissues may have many therapeutic applications but complex tissues are hard to create in vitro. Here, Okano and colleagues report the production of functional cardiac tissue sheets with perfusable blood vessels, which increase the thickness and survival of transplanted tissue.
- Hidekazu Sekine
- , Tatsuya Shimizu
- & Teruo Okano
-
Article |
 A platform pathway for production of 3-hydroxyacids provides a biosynthetic route to 3-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone
A platform pathway for production of 3-hydroxyacids provides a biosynthetic route to 3-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone
3-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone (3HBL) is a building block for many valuable drugs and is synthesized via a costly industrial process. Martin et al. engineer a novel biosynthetic pathway for the inexpensive production of 3HBL and other 3-hydroxyacids in E. coli.
- Collin H. Martin
- , Himanshu Dhamankar
- & Kristala L.J. Prather
-
Article |
 Non-uniform membrane diffusion enables steady-state cell polarization via vesicular trafficking
Non-uniform membrane diffusion enables steady-state cell polarization via vesicular trafficking
The mechanism by which proteins become polarized to a specific cortical site in budding yeast cells has been a topic of recent debate. Slaughter et al.show that differing diffusion rates of Cdc42 within plasma membrane environments sustain the polarized state.
- Brian D. Slaughter
- , Jay R. Unruh
- & Rong Li
-
Article |
 Dimensionality of brain networks linked to life-long individual differences in self-control
Dimensionality of brain networks linked to life-long individual differences in self-control
The ability to delay gratification in childhood correlates with the ability to exert self-control in adulthood. Berman and colleagues re-examine individuals that were studied 40 years ago and find that the individuals who are able to exert a high level of self-control have more efficient neural networks.
- Marc G. Berman
- , Grigori Yourganov
- & John Jonides
-
Article |
 Monitoring and robust induction of nephrogenic intermediate mesoderm from human pluripotent stem cells
Monitoring and robust induction of nephrogenic intermediate mesoderm from human pluripotent stem cells
Stem cells have raised hopes of developing regenerative therapies of renal disease. Here, Osafune et al.provide a protocol for the differentiation of induced human pluripotent stem cells into renal lineages with the capacity to form tubular renal structures in mice.
- Shin-Ichi Mae
- , Akemi Shono
- & Kenji Osafune
-
Article |
 The ghost of nestedness in ecological networks
The ghost of nestedness in ecological networks
A nested pattern of interactions is thought to promote species persistence in mutualistic ecological networks. In this study, Staniczenko et al. introduce a spectral graph measure of nestedness, to show that nestedness is maximally destabilizing and demonstrate that empirical species preferences are not quantitatively nested.
- Phillip P. A. Staniczenko
- , Jason C. Kopp
- & Stefano Allesina
-
Article |
 Environmental conditions and community evenness determine the outcome of biological invasion
Environmental conditions and community evenness determine the outcome of biological invasion
Biological invasion varies under different environmental stressors. Here, using a fully controlled system of bacterial communities, De Roy et al. find that community evenness affects the level of invasion, and that the community’s response depends on specific environmental conditions as well as the community evenness.
- Karen De Roy
- , Massimo Marzorati
- & Nico Boon
-
Article |
 A novel pathway for the production of hydrogen sulfide from D-cysteine in mammalian cells
A novel pathway for the production of hydrogen sulfide from D-cysteine in mammalian cells
Hydrogen sulphide is a signalling molecule with cytoprotective activity in mammals. Here, Kimura and colleagues identify a new biosynthetic pathway for the production of hydrogen sulphide from D-cysteine, which is shown to protect mouse kidneys from oxidative stress after ischaemia/reperfusion injury.
- Norihiro Shibuya
- , Shin Koike
- & Hideo Kimura
-
Article |
 Gender identification of the Mesozoic bird Confuciusornis sanctus
Gender identification of the Mesozoic bird Confuciusornis sanctus
Specimens of the Early Cretaceous bird C. sanctuswith ornamental tail feathers are commonly interpreted as male, and those without as female. In this study, in support of this theory, medullary bone—a tissue unique to reproductively active female birds—is found in a specimen without ornamental feathers.
- Anusuya Chinsamy
- , Luis M. Chiappe
- & Zhang Fengjiao
-
Article |
 The oldest echinoderm faunas from Gondwana show that echinoderm body plan diversification was rapid
The oldest echinoderm faunas from Gondwana show that echinoderm body plan diversification was rapid
The oldest echinoderm faunas have previously been restricted to North America and had a radiate body plan. This discovery of echinoderms from Morocco reveals a diverse range of body forms just 15 million years after echinoderms first evolved a calcite skeleton, showing a rapid rate of morphological evolution.
- Andrew B. Smith
- , Samuel Zamora
- & J. Javier Álvaro
-
Article |
 Reduced plumage and flight ability of a new Jurassic paravian theropod from China
Reduced plumage and flight ability of a new Jurassic paravian theropod from China
Feathered dinosaurs from the Middle-Late Jurassic of north-eastern China have recently been described. Here, a new paravian dinosaur, characterized by less extensive feathers on its limbs and tail, shows that the plumage of theropods was already diversified and adapted to different ecological niches by the Late Jurassic.
- Pascal Godefroit
- , Helena Demuynck
- & Philippe Claeys
-
Article |
 Evolution of the protein stoichiometry in the L12 stalk of bacterial and organellar ribosomes
Evolution of the protein stoichiometry in the L12 stalk of bacterial and organellar ribosomes
The ribosomal stalk L12 is the only multi-copy protein in the ribosome and is essential for translation. Here Davydov et al.use a bioinformatics and mass spectrometry approach to study the evolution of L12 in bacterial ribosomes and predict its stoichiometry in a wide range of species.
- Iakov I. Davydov
- , Ingo Wohlgemuth
- & Marina V. Rodnina
-
Article |
 Analysis of protein-coding mutations in hiPSCs and their possible role during somatic cell reprogramming
Analysis of protein-coding mutations in hiPSCs and their possible role during somatic cell reprogramming
Recent studies have shown that human induced pluripotent stem cells contain point mutations in coding regions, but the functional significance of these mutations is unclear. Here the authors provide evidence that these mutations are unlikely to confer a selective advantage for reprogramming.
- Sergio Ruiz
- , Athurva Gore
- & Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte
-
Article |
 MicroRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance by regulating TWF1 and IL-11
MicroRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance by regulating TWF1 and IL-11
The role of microRNAs in chemotherapy resistance remains to be elucidated. Bockhorn et al.report that microRNA-30c, a human breast tumour prognostic marker, has a key role by targeting the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition promoter twinfilin 1 and downstream interleukin-11 expression.
- Jessica Bockhorn
- , Rachel Dalton
- & Huiping Liu
-
Article |
 A genetically female brain is required for a regular reproductive cycle in chicken brain chimeras
A genetically female brain is required for a regular reproductive cycle in chicken brain chimeras
Sexual dimorphism describes physical differences between males and females of the same species and is partly shaped by the action of hormones. Maekawa and colleagues construct mixed-sex chicken brain chimeras and find that the female reproductive cycle is largely destroyed in female chimeras with male brains.
- Fumihiko Maekawa
- , Miyano Sakurai
- & Hiroko Ohki-Hamazaki
-
Article
| Open Access On-demand optogenetic control of spontaneous seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy
On-demand optogenetic control of spontaneous seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy
Temporal lobe epilepsy in adults does not always respond to treatment. Krook-Magnuson and colleagues use optogenetics to inhibit and activate excitatory and inhibitory neurons, respectively, in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy, and find that they can stop seizures on a moment-to-moment basis.
- Esther Krook-Magnuson
- , Caren Armstrong
- & Ivan Soltesz
-
Article
| Open Access A pairwise maximum entropy model accurately describes resting-state human brain networks
A pairwise maximum entropy model accurately describes resting-state human brain networks
During rest, the different regions of the human brain still carry out complex interactions. In this study, a pairwise maximum entropy model is used to quantify the complexity of these interactions during rest, showing that the model is able to capture the structure of the resting-state human brain networks.
- Takamitsu Watanabe
- , Satoshi Hirose
- & Naoki Masuda
-
Article |
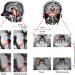 Spatial organization of frequency preference and selectivity in the human inferior colliculus
Spatial organization of frequency preference and selectivity in the human inferior colliculus
Studies in animals have shown that the inferior colliculus of the auditory pathway is tonotopically organized. This fMRI study in humans reveals a low-to-high frequency gradient in the inferior colliculus that is tonotopically oriented, as well as spectral selectivity based on responses to natural sounds.
- Federico De Martino
- , Michelle Moerel
- & Elia Formisano
-
Article
| Open Access Transgenerational gene silencing causes gain of virulence in a plant pathogen
Transgenerational gene silencing causes gain of virulence in a plant pathogen
Plant pathogens encode effector proteins that trigger immunity in plants carrying appropriate resistance genes. Here Qutob et al. show non-Mendelian interactions between naturally occurring Phytophthora sojaealleles that result in transgenerational gene silencing and gain of virulence in soybean plants.
- Dinah Qutob
- , B. Patrick Chapman
- & Mark Gijzen
-
Article
| Open Access Signalling properties of inorganic polyphosphate in the mammalian brain
Signalling properties of inorganic polyphosphate in the mammalian brain
Inorganic polyphosphates have been identified in the central nervous system. Holmström and colleagues examine neuroglial cultures in vitro and cardiorespiratory responses in vivo, and find that inorganic polyphosphates trigger calcium-dependent activation of astrocytes and increase cardiorespiratory activity.
- Kira M. Holmström
- , Nephtali Marina
- & Andrey Y. Abramov
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple pore conformations driven by asynchronous movements of voltage sensors in a eukaryotic sodium channel
Multiple pore conformations driven by asynchronous movements of voltage sensors in a eukaryotic sodium channel
In outwardly rectifying potassium channels, depolarization initiates conformational changes in voltage-sensing domains. Goldschen-Ohmet al. find that movement of three specific domains correlates with conductance levels, and rearrangements of a fourth domain results in preinactivation subconductance states.
- Marcel P. Goldschen-Ohm
- , Deborah L. Capes
- & Baron Chanda
-
Article |
 hVps41 and VAMP7 function in direct TGN to late endosome transport of lysosomal membrane proteins
hVps41 and VAMP7 function in direct TGN to late endosome transport of lysosomal membrane proteins
Delivery of lysosome-associated membrane proteins (LAMPs), is important for lysosome stability and function. Here, Pols et al. identify a previously uncharacterized pathway for transport of lysosome-associated membrane proteins LAMPs directly from the trans-golgi network to late endosomes.
- Maaike S. Pols
- , Eline van Meel
- & Judith Klumperman
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into protein-only RNase P complexed with tRNA
Structural insights into protein-only RNase P complexed with tRNA
RNase P is a key enzyme implicated in transfer RNA maturation that removes the 5′-leader sequences from transfer RNA precursors. In this study, a biophysical characterization of a novel protein-only variant of RNase P, known as PRORP (PROteinaceous RNase P), reveals that transfer RNA recognition by PRORP is similar to that by ribonucleoprotein RNase P.
- Anthony Gobert
- , Franziska Pinker
- & Philippe Giegé
-
Article |
 Interaction between p68 RNA helicase and Ca2+-calmodulin promotes cell migration and metastasis
Interaction between p68 RNA helicase and Ca2+-calmodulin promotes cell migration and metastasis
Cell migration requires motor protein-driven delivery of proteins to the leading edge. This study shows that p68 RNA helicase behaves as a microtubule-based motor upon binding calmodulin, and that blocking this interaction inhibits cancer cell metastasis.
- Haizhen Wang
- , Xueliang Gao
- & Zhi-Ren Liu
-
Article |
 A structural basis for streptomycin-induced misreading of the genetic code
A structural basis for streptomycin-induced misreading of the genetic code
The antibiotic streptomycin increases errors in protein translation, but it is unclear how streptomycin exerts its effect on the ribosome. Demirci et al. present X-ray crystal structures that reveal conformational changes induced by streptomycin, which may inspire future efforts in antibiotics design.
- Hasan Demirci
- , Frank Murphy IV
- & Gerwald Jogl
-
Article
| Open Access Rab9 and retromer regulate retrograde trafficking of luminal protein required for epithelial tube length control
Rab9 and retromer regulate retrograde trafficking of luminal protein required for epithelial tube length control
The development of biological tubes is regulated by mutual interactions between cells and luminal extracellular matrix. Donget al. show that retrograde recycling of luminal chitin deacetylase regulates Drosophila tracheal tubule geometry by restricting length independently of diameter.
- Bo Dong
- , Ken Kakihara
- & Shigeo Hayashi
-
Article |
 Different types of synchrony in chaotic and cyclic communities
Different types of synchrony in chaotic and cyclic communities
Natural populations are complex systems where interactions can lead to chaotic dynamics. This study tests how cyclic and chaotic microbial predator–prey communities synchronize, showing different phase-locking responses for cyclic and chaotic systems.
- Lutz Becks
- & Hartmut Arndt
-
Article |
 Release of SOS2 kinase from sequestration with GIGANTEA determines salt tolerance in Arabidopsis
Release of SOS2 kinase from sequestration with GIGANTEA determines salt tolerance in Arabidopsis
The flowering time and clock-related protein GIGANTEA has been broadly implicated in the development and physiology of plants. Kim and colleagues studyArabidopsisand find that GIGANTEA modulates salt stress via the release of the protein kinase SOS2, which is required for salt tolerance.
- Woe-Yeon Kim
- , Zahir Ali
- & Dae-Jin Yun
-
Article |
 Functional genomics identifies type I interferon pathway as central for host defense against Candida albicans
Functional genomics identifies type I interferon pathway as central for host defense against Candida albicans
Systemic infection with the fungal pathogenC. albicans is characterized by high mortality, and the precise antifungal defence mechanisms in humans are poorly defined. Using a systems approach, Smeekens et al. describe a previously unknown role for type I interferons in human anti-Candidadefence.
- Sanne P. Smeekens
- , Aylwin Ng
- & Ramnik J. Xavier
-
Article |
 Germinal centre protein HGAL promotes lymphoid hyperplasia and amyloidosis via BCR-mediated Syk activation
Germinal centre protein HGAL promotes lymphoid hyperplasia and amyloidosis via BCR-mediated Syk activation
The human germinal centre-associated lymphoma gene is expressed in germinal centre B-lymphocytes; however, its function is unknown. Here the authors show that human germinal centre-associated lymphoma activates Syk kinase, leading to lymphoid hyperplasia and systemic reactive amyloid A amyloidosis in transgenic mice.
- Isabel Romero-Camarero
- , Xiaoyu Jiang
- & Izidore S Lossos
-
Article |
 Splicing factor SRSF3 is crucial for hepatocyte differentiation and metabolic function
Splicing factor SRSF3 is crucial for hepatocyte differentiation and metabolic function
Splicing factors, such as the protein SRSF3, regulate mRNA metabolism but are hard to study in vivobecause genetic kockouts are usually lethal. Here, Sen and colleagues create mice with a hepatocyte-specific knockout of Srsf3 and demonstrate its role in hepatocyte differentiation and liver function.
- Supriya Sen
- , Hassan Jumaa
- & Nicholas J. G. Webster
-
Article
| Open Access A thermoresponsive and chemically defined hydrogel for long-term culture of human embryonic stem cells
A thermoresponsive and chemically defined hydrogel for long-term culture of human embryonic stem cells
To transfer cultured human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) between culture dishes, cells need to be released using mechanical, enzymatic or chemical means, which can damage cells. Zhanget al. describe a thermomodulatable hydrogel that allows gentle, reagent-free cell passaging for the long-term culture of hESCs.
- Rong Zhang
- , Heidi K. Mjoseng
- & Mark Bradley
-
Article
| Open Access The bipolar assembly domain of the mitotic motor kinesin-5
The bipolar assembly domain of the mitotic motor kinesin-5
During mitosis, kinesin-5 motors are thought to crosslink microtubules in a muscle-like sliding filament mechanism. By combining electron microscopy with other structural tools, the authors reveal how four kinesin-5 polypeptides are organized into bipolar minifilaments.
- Seyda Acar
- , David B. Carlson
- & Jonathan M. Scholey
-
Article |
 Extensive diversification of IgH subclass-encoding genes and IgM subclass switching in crocodilians
Extensive diversification of IgH subclass-encoding genes and IgM subclass switching in crocodilians
Different mechanisms for generating antibody diversity have evolved since the emergence of immunoglobulin genes in jawed vertebrates. By sequencing the crocodilian immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus, Chenget al. uncover new insights into the evolutionary origins of adaptive immunity.
- Gang Cheng
- , Yang Gao
- & Yaofeng Zhao
-
Article |
 A safe lithium mimetic for bipolar disorder
A safe lithium mimetic for bipolar disorder
Lithium is commonly used to treat bipolar disorder, but it exerts side effects at doses close to the therapeutic range. Singh and colleagues screen a collection of clinical compounds and find that ebselen induces lithium-like effects on mouse models of bipolar disorder by inhibiting inositol monophosphatase.
- Nisha Singh
- , Amy C. Halliday
- & Grant C. Churchill
-
Article
| Open Access Higher levels of multiple ecosystem services are found in forests with more tree species
Higher levels of multiple ecosystem services are found in forests with more tree species
Tree diversity is thought to benefit forest ecosystems, but evidence from large-scale studies is scarce. This study of a 400,000 km2forest area shows that higher tree species richness supports higher levels of multiple ecosystem services, and therefore also a more sustainable management of production forests.
- Lars Gamfeldt
- , Tord Snäll
- & Jan Bengtsson
-
Article
| Open Access Displays of paternal mouse pup retrieval following communicative interaction with maternal mates
Displays of paternal mouse pup retrieval following communicative interaction with maternal mates
Parental responsibilities in mice are usually carried out by the mother of the pups. In this study, the authors show that when mothers are separated from their mouse pups, they emit ultrasonic vocalizations to their male partners, who respond by administering paternal care to the pups.
- Hong-Xiang Liu
- , Olga Lopatina
- & Haruhiro Higashida
-
Article |
 Kinship reduces alloparental care in cooperative cichlids where helpers pay-to-stay
Kinship reduces alloparental care in cooperative cichlids where helpers pay-to-stay
In alloparental brood care, individuals help raise the offspring of others and it is thought that high relatedness between the helpers and recipients is needed. In contrast, Zöttlet al. find that, in cooperatively breeding cichlids, unrelated subordinate females provide more alloparental care than related ones.
- Markus Zöttl
- , Dik Heg
- & Michael Taborsky
-
Article |
 In vivo imaging of virological synapses
In vivo imaging of virological synapses
In vitro, retroviruses spread between cells via structures resembling synapses. Sewaldet al. now demonstrate that virological synapses can also be observed in living mice by intravital microscopy, validating this concept in vivo.
- Xaver Sewald
- , David G. Gonzalez
- & Walther Mothes
-
Article |
 Activity of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter varies greatly between tissues
Activity of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter varies greatly between tissues
The flow of calcium into the mitochondrial matrix is mediated by the mitochondrial calcium uniporter. Fieniet al. apply patch-clamp techniques to mitoplasts isolated from different mouse and Drosophilatissues and find that the mitochondrial calcium uniporter activity varies depending on the tissue studied.
- Francesca Fieni
- , Sung Bae Lee
- & Yuriy Kirichok
Browse narrower subjects
- Biochemistry
- Biological techniques
- Biophysics
- Biotechnology
- Cancer
- Cell biology
- Chemical biology
- Computational biology and bioinformatics
- Developmental biology
- Drug discovery
- Ecology
- Evolution
- Genetics
- Immunology
- Microbiology
- Molecular biology
- Neuroscience
- Physiology
- Plant sciences
- Psychology
- Stem cells
- Structural biology
- Systems biology
- Zoology

 Spatial association with PTEX complexes defines regions for effector export into Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes
Spatial association with PTEX complexes defines regions for effector export into Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes