Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access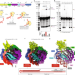 Template and target-site recognition by human LINE-1 in retrotransposition
Template and target-site recognition by human LINE-1 in retrotransposition
Human LINE-1 ORF2p relies on upstream single-stranded target DNA to position the adjacent duplex in the endonuclease active site for nicking of the longer DNA strand, with a single nick generating a staggered DNA break.
- Akanksha Thawani
- , Alfredo Jose Florez Ariza
- & Kathleen Collins
-
News & Views |
 Structures of the amphetamine-binding receptor will aid drug discovery
Structures of the amphetamine-binding receptor will aid drug discovery
High-resolution structures of TAAR1 — the receptor bound by amphetamines and molecules called trace amines — reveal detailed interactions with ligand molecules that will inform efforts to design antipsychotic drugs.
- Harald H. Sitte
-
Article |
 SlyB encapsulates outer membrane proteins in stress-induced lipid nanodomains
SlyB encapsulates outer membrane proteins in stress-induced lipid nanodomains
SlyB, a lipoprotein in the PhoPQ stress regulon in Gram-negative bacteria, forms stable stress-induced complexes with the outer membrane proteome.
- Arne Janssens
- , Van Son Nguyen
- & Han Remaut
-
Article |
 Transport and inhibition mechanisms of human VMAT2
Transport and inhibition mechanisms of human VMAT2
Structures of human vesicular monoamine transporter 2 in complexes with serotonin and three clinical drugs provide insights into the structural basis for serotonin transport and inhibition of transporter activity by the drugs.
- Di Wu
- , Qihao Chen
- & Daohua Jiang
-
News |
 Are your organs ageing well? The blood holds clues
Are your organs ageing well? The blood holds clues
One organ in a person’s body can age faster than the rest — with implications for health and mortality.
- Max Kozlov
-
Article
| Open Access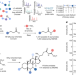 Reverse metabolomics for the discovery of chemical structures from humans
Reverse metabolomics for the discovery of chemical structures from humans
A new discovery strategy, ‘reverse metabolomics’, facilitates high-throughput matching of mass spectrometry spectra in public untargeted metabolomics datasets, and a proof-of-concept experiment identified an association between microbial bile amidates and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Emily C. Gentry
- , Stephanie L. Collins
- & Pieter C. Dorrestein
-
Research Highlight |
 A low-cost electron microscope maps proteins at speed
A low-cost electron microscope maps proteins at speed
Bespoke cryo-electron microscope reveals 3D details of cellular structures — and is an order of magnitude cheaper than its rivals.
-
Research Briefing |
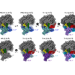 Atomic-level structures show how accuracy is maintained in protein synthesis
Atomic-level structures show how accuracy is maintained in protein synthesis
A series of structures of the eukaryotic protein-synthesis machinery are imaged at high resolution in defined states of the elongation phase of protein synthesis. Analysis suggests that there are underlying molecular mechanisms that increase the accuracy of translation of genetic information in eukaryotes.
-
Article |
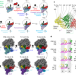 mRNA reading frame maintenance during eukaryotic ribosome translocation
mRNA reading frame maintenance during eukaryotic ribosome translocation
The accuracy of eukaryotic ribosome translocation relies on eukaryote-specific elements of the 80S ribosome, elongation factor 2 and transfer RNAs, all of which contribute to the maintenance of the messenger RNA reading frame.
- Nemanja Milicevic
- , Lasse Jenner
- & Gulnara Yusupova
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into intron catalysis and dynamics during splicing
Structural insights into intron catalysis and dynamics during splicing
Analysis of the group II intron ribonucleoprotein shows the molecular interactions involved in branchpoint adenosine recognition, lariat formation and exon ligation, providing clues to the evolutionary conservation of structural components and catalytic mechanisms in premessenger RNA splicing.
- Ling Xu
- , Tianshuo Liu
- & Anna Marie Pyle
-
Article |
 Recognition and maturation of IL-18 by caspase-4 noncanonical inflammasome
Recognition and maturation of IL-18 by caspase-4 noncanonical inflammasome
Activated human caspase-4 directly and efficiently processes IL-18 in vitro and during bacterial infections, cleaving the same tetrapeptide site in pro-IL-18 as caspase-1.
- Xuyan Shi
- , Qichao Sun
- & Feng Shao
-
Technology Feature |
 Microbial miners take on rare-earth metals
Microbial miners take on rare-earth metals
As a tech-hungry world gobbles up rare-earth elements, researchers are adapting bacteria that can isolate and purify the metals in the absence of harsh chemicals.
- Amber Dance
-
Article
| Open Access The social and structural architecture of the yeast protein interactome
The social and structural architecture of the yeast protein interactome
A protein interaction network constructed with data from high-throughput affinity enrichment coupled to mass spectrometry provides a highly saturated yeast interactome with 31,004 interactions, including low-abundance complexes, membrane protein complexes and non-taggable protein complexes.
- André C. Michaelis
- , Andreas-David Brunner
- & Matthias Mann
-
Article |
 Stepwise requirements for polymerases δ and θ in theta-mediated end joining
Stepwise requirements for polymerases δ and θ in theta-mediated end joining
Polymerase delta is required for multiple steps in polymerase theta-dependent repair of chromosome breaks, a pathway targeted in cancer therapy.
- Susanna Stroik
- , Juan Carvajal-Garcia
- & Dale A. Ramsden
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting multiple conformations via sequence clustering and AlphaFold2
Predicting multiple conformations via sequence clustering and AlphaFold2
An analysis of the evolutionary distribution of predicted structures for the metamorphic protein KaiB using AF-Cluster reveals that both conformations of KaiB were distributed in clusters across the KaiB family.
- Hannah K. Wayment-Steele
- , Adedolapo Ojoawo
- & Dorothee Kern
-
Article
| Open Access Plant carbonic anhydrase-like enzymes in neuroactive alkaloid biosynthesis
Plant carbonic anhydrase-like enzymes in neuroactive alkaloid biosynthesis
We show how neuroactive alkaloids from clubmosses are biosynthesized, which reveals an unexpected role for carbonic anhydrase-like enzymes in alkaloid scaffold formation.
- Ryan S. Nett
- , Yaereen Dho
- & Elizabeth S. Sattely
-
Article |
 Ligand recognition and G-protein coupling of trace amine receptor TAAR1
Ligand recognition and G-protein coupling of trace amine receptor TAAR1
TAAR1 has a rigid consensus binding motif that binds to endogenous trace amine stimuli as well as two extended binding pockets that accommodate diverse chemotypes.
- Zheng Xu
- , Lulu Guo
- & Zhenhua Shao
-
Comment |
 ‘Oceans are hugely complex’: modelling marine microbes is key to climate forecasts
‘Oceans are hugely complex’: modelling marine microbes is key to climate forecasts
Microorganisms are the engines that drive most marine processes. Ocean modelling must evolve to take their biological complexity into account.
- Alessandro Tagliabue
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the native myosin filament in the relaxed cardiac sarcomere
Structure of the native myosin filament in the relaxed cardiac sarcomere
A cryo-electron tomography study reports the structure of thick myosin filaments of mouse cardiac muscle in the relaxed state in situ and the MyBP-C links that connect them with the surrounding thin actin filaments.
- Davide Tamborrini
- , Zhexin Wang
- & Stefan Raunser
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and electromechanical coupling of a voltage-gated Na+/H+ exchanger
Structure and electromechanical coupling of a voltage-gated Na+/H+ exchanger
Upon hyperpolarization, the S4 voltage-sensing segment of sea urchin SLC9C1 moves down, removing inhibition caused by an intracellular helix and enabling Na+/H+ exchange, leading to pH-dependent activation of sAC and sperm chemotaxis.
- Hyunku Yeo
- , Ved Mehta
- & David Drew
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of a sperm-specific solute carrier gated by voltage and cAMP
Structures of a sperm-specific solute carrier gated by voltage and cAMP
This study proposes a molecular mechanism of voltage activation in SLC9C1, a transporter essential for male fertility.
- Valeria Kalienkova
- , Martin F. Peter
- & Cristina Paulino
-
Book Review |
 The plant poisons that shape our daily lives
The plant poisons that shape our daily lives
An exploration of nature’s toxins reveals complex relationships between humans and the plant chemicals we use as foods, medicines and mind-altering drugs.
- Emily Monosson
-
News & Views |
 Protein condensation regulates water availability in cells
Protein condensation regulates water availability in cells
Proteins can condense to form membraneless organelles, which act as vessels for biochemical reactions in cells. An investigation shows that protein condensation is also a cellular mechanism for controlling water availability.
- J. Pedro de Souza
- & Howard A. Stone
-
Article
| Open Access Antiviral type III CRISPR signalling via conjugation of ATP and SAM
Antiviral type III CRISPR signalling via conjugation of ATP and SAM
The Bacteroides fragilis type III CRISPR protein Cmr conjugates ATP to S-adenosyl methionine, generating S-adenosyl methionine (SAM)-AMP, a novel second messenger with a role in antiviral signalling.
- Haotian Chi
- , Ville Hoikkala
- & Malcolm F. White
-
Article
| Open Access Macromolecular condensation buffers intracellular water potential
Macromolecular condensation buffers intracellular water potential
Water thermodynamics drive changes in macromolecular assembly that rapidly restore intracellular water availability in response to physiological fluctuations in temperature, pressure and osmotic strength.
- Joseph L. Watson
- , Estere Seinkmane
- & Emmanuel Derivery
-
Technology Feature |
 Soft-landing methods aim to simplify structural biology
Soft-landing methods aim to simplify structural biology
Linking mass spectrometry with cryo-electron microscopy could transform understanding of complex protein structures — if scientists can show that samples remain intact when they hit their target.
- Michael Eisenstein
-
News & Views |
 How purposeless physics underlies purposeful life
How purposeless physics underlies purposeful life
Evolution by natural selection peerlessly describes how life’s complexity develops — but can it be explained in terms of physics? A new approach suggests it can.
- George F. R. Ellis
-
Article
| Open Access piRNA processing by a trimeric Schlafen-domain nuclease
piRNA processing by a trimeric Schlafen-domain nuclease
The endoribonuclease PUCH, a trimer of Schlafen-like-domain proteins, initiates piRNA processing in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans through 5′-end piRNA precursor cleavage.
- Nadezda Podvalnaya
- , Alfred W. Bronkhorst
- & René F. Ketting
-
Spotlight |
 Changing old viticulture for all the right rieslings
Changing old viticulture for all the right rieslings
Can the French wine industry, built on history and terroir, adapt fast enough to withstand climate change?
- Rachel Nuwer
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering new families and folds in the natural protein universe
Uncovering new families and folds in the natural protein universe
The extent to which the AlphaFold database has structurally illuminated proteins that are challenging to annotate for function or putative biological role using standard homology-based approaches at high predicted accuracy is investigated.
- Janani Durairaj
- , Andrew M. Waterhouse
- & Joana Pereira
-
Article |
 A cross-species proteomic map reveals neoteny of human synapse development
A cross-species proteomic map reveals neoteny of human synapse development
A study presents a cross-species proteomic map of synapse development in neocortex and reveals that the human postsynaptic density assembly develops two to three times slower than that in macaques and mice.
- Li Wang
- , Kaifang Pang
- & Arnold R. Kriegstein
-
News & Views |
 Previously unknown pathway for lipid biosynthesis discovered
Previously unknown pathway for lipid biosynthesis discovered
The pathway used by mammalian cells to make triglyceride lipids when supplies of fat molecules are high has long been known. A route that works when fat supplies are low has now been discovered.
- Jean E. Schaffer
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of an alternative triglyceride biosynthesis pathway
Identification of an alternative triglyceride biosynthesis pathway
Triacylglycerols are an energy source produced in humans by DGAT1 and DGAT2, but disrupting these enzymes reveals a noncanonical pathway involving the protein DIESL (formerly TMEM68) and its regulator TMX1, which is important during lipid scarcity.
- Gian-Luca McLelland
- , Marta Lopez-Osias
- & Thijn R. Brummelkamp
-
Article |
 Metabolic programs of T cell tissue residency empower tumour immunity
Metabolic programs of T cell tissue residency empower tumour immunity
A study describes the metabolic adaptations supporting differentiation, survival and function of tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells and how to leverage them to enhance immunity against pathogens and tumours.
- Miguel Reina-Campos
- , Maximilian Heeg
- & Ananda W. Goldrath
-
Article
| Open Access LTP induction by structural rather than enzymatic functions of CaMKII
LTP induction by structural rather than enzymatic functions of CaMKII
Several independent lines of evidence demonstrated long-term potentiation induction by a structural function of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II rather than by its enzymatic activity.
- Jonathan E. Tullis
- , Matthew E. Larsen
- & K. Ulrich Bayer
-
Article
| Open Access A viral ADP-ribosyltransferase attaches RNA chains to host proteins
A viral ADP-ribosyltransferase attaches RNA chains to host proteins
Bacteriophage T4 uses an enzyme known as ADP-ribosyltransferase ModB to modify the translational apparatus of bacteria it infects, not only by ADP-ribosylating proteins, but also by attaching entire RNA chains in a process known as RNAylation.
- Maik Wolfram-Schauerte
- , Nadiia Pozhydaieva
- & Katharina Höfer
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of the conformational states of PIEZO1
Direct observation of the conformational states of PIEZO1
The plasma membrane can expand the blades of the PIEZO1 ion channel, impacting channel activation.
- Eric M. Mulhall
- , Anant Gharpure
- & Ardem Patapoutian
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial integrated stress response controls lung epithelial cell fate
Mitochondrial integrated stress response controls lung epithelial cell fate
This study highlights the role of mitochondrial complex I-dependent NAD+ regeneration in directing lung epithelial cell fate during postnatal alveolar development by preventing pathological integrated stress response induction.
- SeungHye Han
- , Minho Lee
- & Navdeep S. Chandel
-
Article
| Open Access Tail engagement of arrestin at the glucagon receptor
Tail engagement of arrestin at the glucagon receptor
Structures of the glucagon receptor bound to β-arrestin 1 are reported, providing further information about the arrestin-mediated modulation of G protein-coupled receptors.
- Kun Chen
- , Chenhui Zhang
- & Beili Wu
-
News & Views |
 Improved theory of ocean iron cycle resolves modelling issues
Improved theory of ocean iron cycle resolves modelling issues
A revised conceptual model of the chemical and physical forms of iron in the ocean reconciles the mismatch between observations and simulations of the amount of dissolved iron in seawater — and might aid climate predictions.
- Brandy M. Toner
-
Article
| Open Access Central role of Tim17 in mitochondrial presequence protein translocation
Central role of Tim17 in mitochondrial presequence protein translocation
Tim17 contains conserved negative charges close to the intermembrane space side of the bilayer, which are essential to initiate presequence protein translocation along a distinct transmembrane cavity of Tim17 for both classes of preproteins.
- Laura F. Fielden
- , Jakob D. Busch
- & Nils Wiedemann
-
Article |
 Oligomerization-mediated activation of a short prokaryotic Argonaute
Oligomerization-mediated activation of a short prokaryotic Argonaute
Cryo-electron microscopy structures and biochemical analyses provide insight into how short prokaryotic Argonaute proteins are assembled and activated, and reveal that oligomerization has a key role in driving catalytic activity.
- Zhangfei Shen
- , Xiao-Yuan Yang
- & Tian-Min Fu
-
Article |
 Structure of an endogenous mycobacterial MCE lipid transporter
Structure of an endogenous mycobacterial MCE lipid transporter
Proteins of the Mycobacterium smegmatis Mce1 system assemble to form an elongated ABC transporter complex that is long enough to span the impermeable mycobacterial cell envelope.
- James Chen
- , Alice Fruhauf
- & Damian C. Ekiert
-
News & Views |
 Sixty years since the report of global lead pollution
Sixty years since the report of global lead pollution
The 1963 discovery that even the vast oceans were highly contaminated with lead from car exhausts sparked debate and policy changes that benefited the health of millions — and revolutionized the practices of marine biogeochemistry.
- Jerome Nriagu
-
News |
 Dementia risk linked to blood-protein imbalance in middle age
Dementia risk linked to blood-protein imbalance in middle age
Abnormal levels of certain proteins — many of which have roles outside the brain — could be an early hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease or similar conditions.
- Lilly Tozer
-
Research Briefing |
 Protein folding stability measured at scale
Protein folding stability measured at scale
Protein sequences vary widely in their folding stabilities (the energetic favourability of folded compared with unfolded conformations), and protein alterations that affect stability have profound effects on evolution, health and disease, and biotechnological applications. An innovative method has made it possible to measure these stabilities on a massive scale, revealing evolutionary trends and opening up possibilities for machine learning.
-
Article
| Open Access Mega-scale experimental analysis of protein folding stability in biology and design
Mega-scale experimental analysis of protein folding stability in biology and design
Large-scale assays using cDNA display proteolysis are used to measure the folding stabilities of protein domains, providing a method to quantify the effects of mutations on protein folding, with applications in protein design.
- Kotaro Tsuboyama
- , Justas Dauparas
- & Gabriel J. Rocklin
-
News Feature |
 AI tools are designing entirely new proteins that could transform medicine
AI tools are designing entirely new proteins that could transform medicine
Digital art techniques can now devise custom, working biomolecules on demand.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Article
| Open Access De novo design of protein structure and function with RFdiffusion
De novo design of protein structure and function with RFdiffusion
Fine-tuning the RoseTTAFold structure prediction network on protein structure denoising tasks yields a generative model for protein design that achieves outstanding performance on a wide range of protein structure and function design challenges.
- Joseph L. Watson
- , David Juergens
- & David Baker
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biocatalysis
- Biogeochemistry
- Bioinorganic chemistry
- Biophysical chemistry
- Carbohydrates
- Chemical modification
- Cytokines
- DNA
- Enzyme mechanisms
- Enzymes
- Glycobiology
- Glycomics
- Histocytochemistry
- Hormones
- Immunochemistry
- Ion channels
- Isoenzymes
- Kinases
- Lipidomics
- Lipids
- Metabolomics
- Metals
- Neurochemistry
- Peptides
- Prions
- Proteases
- Protein folding
- Proteins
- Proteolysis
- Proteomics
- RNA
- Structural biology

 De novo design of high-affinity binders of bioactive helical peptides
De novo design of high-affinity binders of bioactive helical peptides