Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Epithelial IFNγ signalling and compartmentalized antigen presentation orchestrate gut immunity
Epithelial IFNγ signalling and compartmentalized antigen presentation orchestrate gut immunity
IFNγ signalling in epithelial cells promotes antigen presentation that confers intra-epithelial T cells the ability to limit extracellular ATP and consequent NLRP3 inflammasome activation, controlling pathogenic transformation of CD4+ T cells that promotes colitis and colorectal cancer in mouse models.
- Ankit Malik
- , Deepika Sharma
- & Bana Jabri
-
Article |
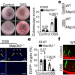 MAP3K2-regulated intestinal stromal cells define a distinct stem cell niche
MAP3K2-regulated intestinal stromal cells define a distinct stem cell niche
A subset of intestinal stromal cells that is regulated by the kinase MAP3K2 protects intestinal stem cells against injury by producing the WNT agonist R-spondin 1.
- Ningbo Wu
- , Hongxiang Sun
- & Bing Su
-
Article |
 Exuberant fibroblast activity compromises lung function via ADAMTS4
Exuberant fibroblast activity compromises lung function via ADAMTS4
Viral infection of the respiratory system induces exuberant fibroblast activity, resulting in extensive remodelling of the extracellular matrix and cytokine release, which promote immune cell infiltration of the affected area at the expense of respiratory function.
- David F. Boyd
- , E. Kaitlynn Allen
- & Paul G. Thomas
-
Article |
 Sex differences in immune responses that underlie COVID-19 disease outcomes
Sex differences in immune responses that underlie COVID-19 disease outcomes
Male patients with COVID-19 have higher plasma levels of innate immune cytokines and chemokines such as IL-8, IL-18 and CCL5 and more non-classical monocytes than female patients, whereas female patients mount robust T cell activation maintained even in older age.
- Takehiro Takahashi
- , Mallory K. Ellingson
- & Akiko Iwasaki
-
Letter |
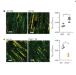 Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation
Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation
Acute and chronic mitochondrial stress in mice require PINK1 and parkin to restrain STING-mediated innate immunity.
- Danielle A. Sliter
- , Jennifer Martinez
- & Richard J. Youle
-
Letter |
 Precision editing of the gut microbiota ameliorates colitis
Precision editing of the gut microbiota ameliorates colitis
Tungstate inhibits molybdenum-cofactor-dependent microbial respiratory pathways and shows potential as a selective treatment for microbial imbalances that occur during inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Wenhan Zhu
- , Maria G. Winter
- & Sebastian E. Winter
-
Article |
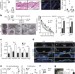 Inflammatory memory sensitizes skin epithelial stem cells to tissue damage
Inflammatory memory sensitizes skin epithelial stem cells to tissue damage
After acute inflammation, epithelial stem cells retain a memory that accelerates restoration of the skin barrier during subsequent tissue damage, and this enhancement is dependent on the AIM2 inflammasome and its downstream effectors.
- Shruti Naik
- , Samantha B. Larsen
- & Elaine Fuchs
-
Letter |
 Feedback control of AHR signalling regulates intestinal immunity
Feedback control of AHR signalling regulates intestinal immunity
Cytochrome P4501 enzymes have a role in the regulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand levels in the gut, affecting innate lymphoid and TH17 cell responses.
- Chris Schiering
- , Emma Wincent
- & Brigitta Stockinger
-
Letter |
 Unique role for ATG5 in neutrophil-mediated immunopathology during M. tuberculosis infection
Unique role for ATG5 in neutrophil-mediated immunopathology during M. tuberculosis infection
Genetic engineering in mice reveals that autophagy is not an essential mechanism in myeloid cells for controlling Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, and that autophagy factor ATG5 protects organisms by regulating neutrophil influx and tissue damage.
- Jacqueline M. Kimmey
- , Jeremy P. Huynh
- & Christina L. Stallings
-
Letter |
 Dendritic cells control fibroblastic reticular network tension and lymph node expansion
Dendritic cells control fibroblastic reticular network tension and lymph node expansion
During inflammation, the lymph node stromal compartment is shown to accommodate high numbers of infiltrating lymphocytes by relaxing the cytoskeleton of fibroblastic reticular cells, allowing the latter to stretch and the lymph node to expand.
- Sophie E. Acton
- , Aaron J. Farrugia
- & Caetano Reis e Sousa
-
Review Article |
 Nucleotide signalling during inflammation
Nucleotide signalling during inflammation
Extracellular ATP released from cells during inflammatory responses predominantly functions as a signalling molecule through the activation of purinergic P2 receptors and contributes to both beneficial and detrimental inflammatory responses; this review examines P2 receptor signalling via ATP and its effect on the outcome of inflammatory and infectious diseases.
- Marco Idzko
- , Davide Ferrari
- & Holger K. Eltzschig
-
Letter |
 Neutrophil swarms require LTB4 and integrins at sites of cell death in vivo
Neutrophil swarms require LTB4 and integrins at sites of cell death in vivo
Two-photon intravital imaging is used here to define the regulation of interstitial neutrophil migration at local sites of cell death upon sterile tissue injury and infection; leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is shown to act between neutrophils as a signal relay molecule that acts to enhance the radius of neutrophil recruitment within the inflamed interstitium, and also to control, in concert with integrin receptors, dense neutrophil clustering for tight wound seal formation.
- Tim Lämmermann
- , Philippe V. Afonso
- & Ronald N. Germain
-
Outlook |
 Health impact: Breathless
Health impact: Breathless
COPD is one of the world's biggest killers, but awareness is low, diagnosis is often missed, and in many countries the extent of the problem is not even well-documented.
- Amber Dance
-
Outlook |
 Perspective: Clues, not conclusions
Perspective: Clues, not conclusions
Scientists have some way to go before they can prove that COPD should be treated as an autoimmune disease, says Steven R. Duncan.
- Steven R. Duncan
-
Article |
 Gut inflammation provides a respiratory electron acceptor for Salmonella
Gut inflammation provides a respiratory electron acceptor for Salmonella
Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium causes acute gut inflammation, which promotes the growth of the pathogen through unknown mechanisms. It is now shown that the reactive oxygen species generated during inflammation react with host-derived sulphur compounds to produce tetrathionate, which the pathogen uses as a terminal electron acceptor to support its growth. The ability to use tetrathionate provides the pathogen with a competitive advantage over bacteria that lack this property.
- Sebastian E. Winter
- , Parameth Thiennimitr
- & Andreas J. Bäumler

 Multimodal decoding of human liver regeneration
Multimodal decoding of human liver regeneration