Article |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Formin-mediated nuclear actin at androgen receptors promotes transcription
Formin-mediated nuclear actin at androgen receptors promotes transcription
Functional mutations identified in patients with androgen insensitivity syndrome, in the formin and actin nucleator DAAM2, uncover signal-regulated nuclear actin assembly at a steroid hormone receptor necessary for transcription.
- Julian Knerr
- , Ralf Werner
- & Nadine C. Hornig
-
Article
| Open Access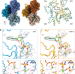 Bending forces and nucleotide state jointly regulate F-actin structure
Bending forces and nucleotide state jointly regulate F-actin structure
The nucleotide state of actin modulates F-actin structural transitions evoked by bending forces.
- Matthew J. Reynolds
- , Carla Hachicho
- & Gregory M. Alushin
-
Article |
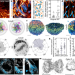 Actin cables and comet tails organize mitochondrial networks in mitosis
Actin cables and comet tails organize mitochondrial networks in mitosis
During mitosis, complementary actin-based mechanisms ensure equal and random distributions of mitochondria among daughter cells following symmetrical cell division.
- Andrew S. Moore
- , Stephen M. Coscia
- & Erika L. F. Holzbaur
-
Article |
 Cooperative epithelial phagocytosis enables error correction in the early embryo
Cooperative epithelial phagocytosis enables error correction in the early embryo
Mechanical load-sharing enables the long-range cooperative uptake of apoptotic cells by multiple epithelial cells; and clearance of these apoptotic cells facilitates error correction, which is necessary for developmental robustness and survival of the embryo.
- Esteban Hoijman
- , Hanna-Maria Häkkinen
- & Verena Ruprecht
-
Article |
 Mechanical regulation of glycolysis via cytoskeleton architecture
Mechanical regulation of glycolysis via cytoskeleton architecture
Glycolysis in normal epithelial cells responds to microenvironmental mechanics via the modulation of actin bundles that sequester the phosphofructokinase-targeting ubiquitin ligase TRIM21, a process superseded by persistent actin bundles in cancer cells.
- Jin Suk Park
- , Christoph J. Burckhardt
- & Gaudenz Danuser
-
Article |
 Insights into the assembly and activation of the microtubule nucleator γ-TuRC
Insights into the assembly and activation of the microtubule nucleator γ-TuRC
The cryo-EM structure of the γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC) from Xenopus laevis provides insights into the molecular organization of the complex, and shows that actin is a structural component that is functionally relevant to microtubule nucleation.
- Peng Liu
- , Erik Zupa
- & Elmar Schiebel
-
Letter |
 SETD3 is an actin histidine methyltransferase that prevents primary dystocia
SETD3 is an actin histidine methyltransferase that prevents primary dystocia
SETD3 methylates mammalian actin at His73, and SETD3 deficiency impairs stimulus-induced contraction in primary human uterine smooth muscle cells and leads to maternal dystocia in mice.
- Alex W. Wilkinson
- , Jonathan Diep
- & Or Gozani
-
Letter |
 A non-canonical Notch complex regulates adherens junctions and vascular barrier function
A non-canonical Notch complex regulates adherens junctions and vascular barrier function
The transmembrane domain of NOTCH1 plays a key role in the assembly of adherens junctions and the non-transcriptional regulation of vascular permeability that links transcriptional programs with adhesive and cytoskeletal remodelling.
- William J. Polacheck
- , Matthew L. Kutys
- & Christopher S. Chen
-
Letter |
 Rho GTPase complementation underlies BDNF-dependent homo- and heterosynaptic plasticity
Rho GTPase complementation underlies BDNF-dependent homo- and heterosynaptic plasticity
The three small GTPases Rac1, RhoA and Cdc42 are differentially involved in structural long-term potentiation of rodent dendritic spines, simultaneously ensuring signal specificity and also priming the system for plasticity.
- Nathan G. Hedrick
- , Stephen C. Harward
- & Ryohei Yasuda
-
Letter |
 Cryo-EM structure of a human cytoplasmic actomyosin complex at near-atomic resolution
Cryo-EM structure of a human cytoplasmic actomyosin complex at near-atomic resolution
The first high-resolution structure of a human actomyosin complex reveals the interface between F-actin and myosin in near-atomic detail.
- Julian von der Ecken
- , Sarah M. Heissler
- & Stefan Raunser
-
Letter |
 Structure of the F-actin–tropomyosin complex
Structure of the F-actin–tropomyosin complex
Electron cryomicroscopy reveals the three-dimensional structure of F-actin at a resolution of 3.7 Å in complex with tropomyosin at a resolution of 6.5 Å; the stabilizing interactions and the effects of disease-causing mutants are also investigated.
- Julian von der Ecken
- , Mirco Müller
- & Stefan Raunser
-
Letter |
 Dendritic cells control fibroblastic reticular network tension and lymph node expansion
Dendritic cells control fibroblastic reticular network tension and lymph node expansion
During inflammation, the lymph node stromal compartment is shown to accommodate high numbers of infiltrating lymphocytes by relaxing the cytoskeleton of fibroblastic reticular cells, allowing the latter to stretch and the lymph node to expand.
- Sophie E. Acton
- , Aaron J. Farrugia
- & Caetano Reis e Sousa
-
Letter |
 Inhibitory signalling to the Arp2/3 complex steers cell migration
Inhibitory signalling to the Arp2/3 complex steers cell migration
A new protein, Arpin, is identified that inhibits the Arp2/3 complex and controls cell migration by decreasing cell speed and the directional persistence of migration; this inhibitory circuit is under the control of the small GTPase Rac1, and Arpin depletion causes faster lamellipodia protrusion and increased cell migration.
- Irene Dang
- , Roman Gorelik
- & Alexis Gautreau
-
News & Views |
 Actin' dangerously
Actin' dangerously
Recognition of aberrant cell death is a crucial function of the immune system. It seems that one way in which immune cells identify damage is by sensing actin, an abundant intracellular protein.
- Gordon D. Brown
-
Letter |
 Multi-isotope imaging mass spectrometry reveals slow protein turnover in hair-cell stereocilia
Multi-isotope imaging mass spectrometry reveals slow protein turnover in hair-cell stereocilia
Multi-isotope imaging mass spectrometry is used to quantify protein turnover in animal stereocilia, showing that rapid turnover occurs only in stereocilia tips.
- Duan-Sun Zhang
- , Valeria Piazza
- & Claude P. Lechene
-
Letter |
 Mechanical strain in actin networks regulates FilGAP and integrin binding to filamin A
Mechanical strain in actin networks regulates FilGAP and integrin binding to filamin A
- A. J. Ehrlicher
- , F. Nakamura
- & T. P. Stossel
-
Article |
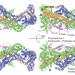 Structure and control of the actin regulatory WAVE complex
Structure and control of the actin regulatory WAVE complex
In cells, WAVE protein, a central regulator of actin dynamics during cell motility, is constitutively incorporated into WAVE regulatory complex (WRC), is normally present in an inactive state and can be activated by a number of inputs. These authors present the structure and mechanistic analysis of WRC. The combined data reveal how the WAVE protein is inhibited within the WRC complex and provide mechanisms for WRC activation at the plasma membrane.
- Zhucheng Chen
- , Dominika Borek
- & Michael K. Rosen
-
Research Highlights |
Molecular biology: Proteins actin' differently
-
News |
 Nanotubes help cells pass messages
Nanotubes help cells pass messages
Actin cables transmit electrical signals between cells.
- Amy Maxmen
-
Letter |
 Direct visualization of secondary structures of F-actin by electron cryomicroscopy
Direct visualization of secondary structures of F-actin by electron cryomicroscopy
The formation of filamentous F-actin, through polymerization of globular G-actin, is essential for processes such as cell motility and muscle contraction. These authors report the structure of F-actin as visualized by electron cryomicroscopy, and build a complete atomic model of F-actin. This new structure will improve our understanding of the mechanism of actin assembly and disassembly.
- Takashi Fujii
- , Atsuko H. Iwane
- & Keiichi Namba
-
News & Views |
 Actin filaments up against a wall
Actin filaments up against a wall
The front of motile cells is thought to be pushed out by branched filaments of actin protein abutting the cell membrane. New work challenges this textbook view, showing that actin branches grow away from, or obliquely to, a surface.
- Cécile Sykes
- & Julie Plastino
-
Letter |
 Mical links semaphorins to F-actin disassembly
Mical links semaphorins to F-actin disassembly
Semaphorins and their receptors, plexins, relay guidance information to neurons during development and regulate actin dynamics through an unknown mechanism. Recently, proteins of the Mical family of enzymes have been found to associate with plexins; here, Mical is reported to directly link semaphorins and their plexin receptors to the precise control of actin filament dynamics.
- Ruei-Jiun Hung
- , Umar Yazdani
- & Jonathan R. Terman

 Mechanics of human embryo compaction
Mechanics of human embryo compaction