Abstract
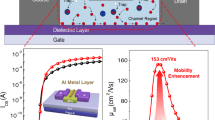
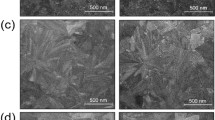
Compared to polycrystalline semiconductors, amorphous semiconductors offer inherent cost-effective, simplicity, and uniform manufacturing. Traditional amorphous hydrogenated Si falls short in electrical properties, necessitating the exploration of new materials. The creation of high-mobility amorphous n-type metal oxides, such as a-InGaZnO1, and their integration into thin-film transistors (TFTs) have propelled advancements in modern large-area electronics and new-generation displays2–8. However, finding comparable p-type counterparts poses significant challenges, impeding the progress of complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology and integrated circuits9–11. Here, we introduce a pioneering design strategy for amorphous p-type semiconductors, incorporating high-mobility tellurium within an amorphous tellurium sub-oxide matrix, and demonstrate its utility in high-performance, stable p-channel TFTs, and complementary circuits. Theoretical analysis unveils a delocalised valence band from tellurium 5p bands with shallow acceptor states, enabling excess hole doping and transport. Selenium alloying suppresses hole concentrations and facilitates the p orbital connectivity, realising high-performance p-channel TFTs with an average field-effect hole mobility of ~15 cm2 V−1 s−1 and on/off current ratios of 106 ~ 107, along with wafer-scale uniformity and long-term stabilities under bias stress and ambient aging. This study represents a crucial stride towards establishing commercially viable amorphous p-channel TFT technology and complementary electronics in a low-cost and industry-compatible manner.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Information, including Supplementary Figures 1-4, Supplementary Tables 1-2, and additional references.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, A., Kim, YS., Kim, M.G. et al. Selenium alloyed tellurium oxide for amorphous p-channel transistors. Nature (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07360-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07360-w
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.