Abstract
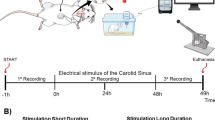
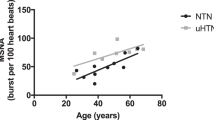
In resistant hypertensive patients acute carotid baroreflex stimulation is associated with a blood pressure (BP) reduction, believed to be mediated by a central sympathoinhbition.The evidence for this sympathomodulatory effect is limited, however. This meta-analysis is the first to examine the sympathomodulatory effects of acute carotid baroreflex stimulation in drug-resistant and uncontrolled hypertension, based on the results of microneurographic studies. The analysis included 3 studies assessing muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA) and examining 41 resistant uncontrolled hypertensives. The evaluation included assessment of the relationships between MSNA and clinic heart rate and BP changes associated with the procedure. Carotid baroreflex stimulation induced an acute reduction in clinic systolic and diastolic BP which achieved statistical significance for the former variable only [systolic BP: −19.98 mmHg (90% CI, −30.52, −9.43), P < 0.002], [diastolic BP: −5.49 mmHg (90% CI, −11.38, 0.39), P = NS]. These BP changes were accompanied by a significant MSNA reduction [−4.28 bursts/min (90% CI, −8.62, 0.06), P < 0.07], and by a significant heart rate decrease [−3.65 beats/min (90% CI, −5.49, −1.81), P < 0.001]. No significant relationship was detected beween the MSNA, systolic and diastolic BP changes induced by the procedure, this being the case also for heart rate. Our data show that the acute BP lowering responses to carotid baroreflex stimulation, although associated with a significant MSNA reduction, are not quantitatively related to the sympathomoderating effects of the procedure. This may suggest that these BP effects depend only in part on central sympathoinhibition, at least in the acute phase following the intervention.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nishikawa T, Omura M, Saito J, Matsuzawa Y. The possibility of resistant hypertension during the treatment of hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res. 2013;36:924–9.
Esler MD. Sympathetic nervous system moves toward center stage in cardiovascular medicine. Hypertension. 2014;63:e25–e32.
Grassi G, Bombelli M, Buzzi S, Volpe M, Brambilla M. Neuroadrenergic disarray in pseudo-resistant and resistant hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2014;37:479–83.
Dudenbostel T, Acelajado MC, Pisoni R, Li P, Oparil S, Calhoun D. Refractory hypertension: evidence of heightened sympathetic activity as a cause of antihypertensive treatment failure. Hypertension. 2015;66:126–33.
Grassi G, Mark A, Esler M. The sympathetic nervous system alterations in human hypertension. Circ Res. 2015;116:976–90.
Dell’Oro R, Quarti-Trevano F, Seravalle G, Bertoli S, Airoldi F, Mancia G, et al. Sympathetic nerve traffic and arterial baroreflex function in apparent drug-resistant hypertension. Hypertension. 2019;74:903–9.
Mancia G, Mark AL. Arterial baroreflexes in humans. In: Shepherd JT, Abboud FM, eds. Handbook of Physiology, Section 2: The cardiovascular system. Bethesda, Md: American Physiological Society; 1983. pp. 755–93.
Bisognano JD, Bakris G, Nadim MK, Sanchez L, Kroon AA, Schafer J, et al. Baroreflex activation therapy lowers blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension: results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled rheos pivotal trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:765–73.
Spiering, Williams W, Heyden B, der JV, Kleef, van M, Lo R, Versmissen J, et al. Endovascular baroreflex amplification for resistant hypertension: a safety and proof-of-principle clinical study. Lancet. 2017;390:2655–61.
Wallbach M, Lehning LY, Schroer C, Luders S, Bohning E, Muller GA, et al. Effects of baroreflex activation therapy on ambulatory blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension. Hypertension. 2016;67:701–9.
Wallback M, Koziolek MJ. Baroreceptors in the carotid and hypertension – systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of baroreflex activation therapy on blood pressure. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2019;33:1485–93.
Lohmeier TE, Irwin ED, Rossing MA, Serdar DJ, Kieval RS. Stimulation of the baroreflex produces sustained hypotension. Hypertension. 2004;43:306–11.
Grassi G. Assessment of sympathetic cardiovascular drive in human hypertension: achievements and perspectives. Hypertension. 2009;54:690–97.
Page MJ, Moher D. Evaluations of the uptake and impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement and extensions: a scoping review. Syst Rev. 2017;6:263.
Heusser K, Tank J, Engeli S, Diedrich A, Menne J, Eckert S, et al. Carotid baroreceptor stimulation, sympathetic activity, baroreflex function, and blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 2010;55:619–26.
Heusser K, Tank J, Brinkmann J, Menne J, Kaufeld J, Linnenweber-Held S, et al. Acute response to unilateral unipolar electrical carotid sinus stimulation in patients with resistant arterial hypertension. Hypertension. 2016;67:585–91.
Heusser K, Thöne A, Lipp A, Menne J, Beige J, Reuter H, et al. Efficacy of electrical baroreflex activation is independent of peripheral chemoreceptor modulation. Hypertension. 2020;75:257–64.
Van Kleef MEAM, Heusser K, Diedrich A, Oey PL, Tank J, Jordan J, et al. Endovascular baroreflex amplification and the effect on sympathetic nerve activity in patients with resistant hypertension. A proof-of-principle study. PloS One. 2021;16:e0259826.
Grassi G, D’Arrigo G, Pisano A, Bolignano D, Mallamaci F, Dell’Oro R, et al. Sympathetic neural overdrive in congestive heart failure and its correlates: systematic reviews and meta-analysis. J Hypertens. 2019;37:1746–56.
Biffi A, Quarti-Trevano F, Bonzani M, Seravalle G, Corrao G, Mancia G, et al. Neuroadrenergic activation in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome A new selected meta-analysis revisited. J Hypertens. 2022;40:15–23.
Grassi G, Biffi A, Dell’Oro R, Quarti Trevano F, Seravalle G, Corrao G, et al. Sympathetic neural abnormalities in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hypertens. 2020;38:1436–42.
Der Simonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–188.
Cochran WG. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics. 1954;10:101–29.
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta- analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–60.
Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of Interventions version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2011. http://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org. Accessed October 9 2023.
Lohmeier TE, Iliescu R, Dwyer TM, Irwin ED, Cates AW, Rossing MA. Sustained suppression of sympathetic activity and arterial pressure during chronic activation of the carotid baroreflex. Am J Physiol. 2010;299:H402–H9.
Laragh JH, Sealey JE. The plasma renin test reveals the contribution of body sodium- volume content (V) and renin-angiotensin (R) vasoconstriction to long-term blood pressure. Am J Hypertens. 2011;24:1164–80.
Grassi G, Dell’Oro R, Bombelli M, Cuspidi C, Quarti-Trevano F. High blood pressure with elevated heart rate: a high risk ”sympathetic” clinical phenotype. Hypertens Res. 2023;46:2318–25.
Gronda E, Seravalle G, Brambilla G, Costantino G, Casini A, Trevano FQ, et al. Chronic baroreflex activation effects on sympathetic nerve traffic, baroreflex function and cardiac haemodynamics in heart failure: a proof-of-concept study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2014;16:977–83.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Biffi, A., Quarti-Trevano, F., Vanoli, J. et al. Effects of acute carotid baroreceptor stimulation on sympathetic nerve traffic in resistant and uncontrolled hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertens Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-024-01704-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-024-01704-9